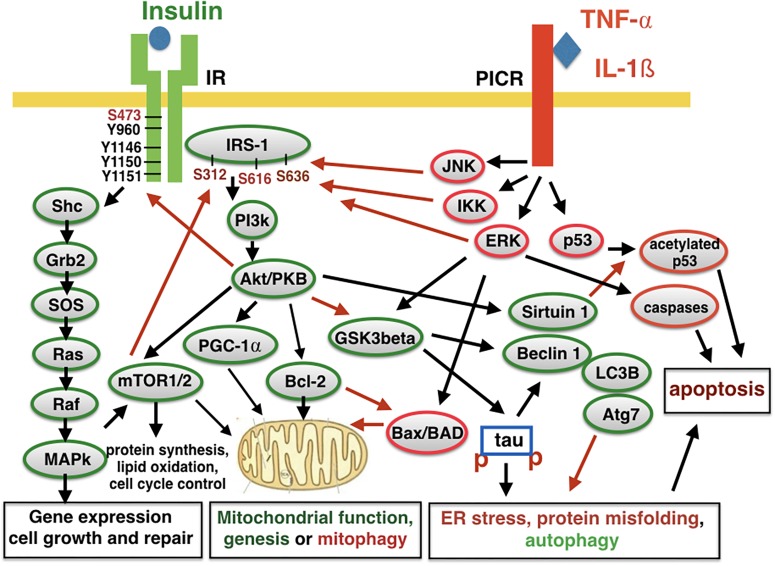
FIGURE 1.
Insulin signaling and pro-inflammatory signaling counteract each other. The activation of the insulin receptor (IR) leads to auto-phosphorylation and activation. Several other kinases can activate or inactivate the receptor. The insulin-receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) also contains several phosphorylation sites that can activate or inhibit second messenger signaling. Downstream signaling activates key physiological processes such as energy utilization, mitochondrial function and replacement, protein synthesis, autophagy, and inhibiting autophagy. Activating pro-inflammatory cytokine receptors (PICR) counteracts these processes and enhances mitophagy, autophagy, and apoptosis. Kinases such as JNK and IKK can phosphorylate IRS-1 to inhibit insulin signaling and induce insulin de-sensitization. IL-1ß, interleukin 1ß; TNF-α, tumor necrosis factor a; JNK, NH2-terminal c-Jun kinase; IKK, inhibitor of kappa B kinase; ERK, extracellular regulated kinase; MAPK, mitogen activated protein kinase; SHP-2, Src-like homology 2(SH2) domain containing protein tyrosine phosphatase; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1-α; Grb2, growth factor receptor binding protein 2; SOS, son of sevenless protein; PI3K, phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; IRS, insulin receptor substrate; PKB, protein kinase B,also known as Akt; Raf, regulation of alpha-fetoprotein; Ras, rat sarcoma virus peptide; LC3B, microtubule-associated proteins 1A/1B light chain 3B; Atg7, autophagy-related protein 7; Bcl-2, B-cell lymphoma 2; Bad, Bcl-2-associated death promoter; Bax, Bcl-2 associated X protein; Shc, Src homology collagen peptide. Red arrows, inhibiting activity; Black arrows, activating activity.