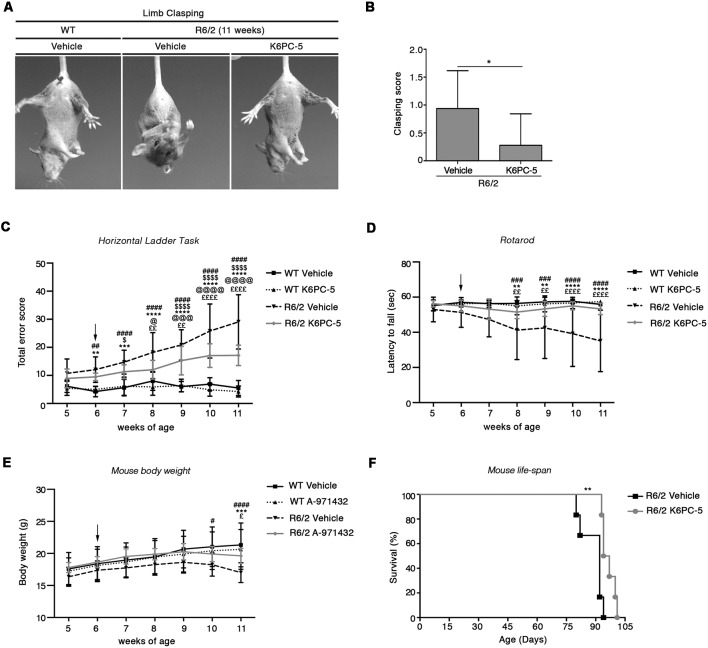
Figure 1.
Administration of K6PC-5 ameliorates Huntington’s disease (HD) mouse phenotype. (A,B) Limb-clasping response at 11 weeks of age HD. Vehicle-treated R6/2 mice, N = 8; K6PC-5-treated R6/2 mice, N = 9. Values are represented as mean ± SD. *p < 0.05 (Un-paired t-test). Motor performance assessed by (C) Horizontal Ladder Task and (D) Rotarod. Vehicle-treated wild-type (WT) mice, N = 8; K6PC-5-treated WT mice, N = 8; vehicle-treated R6/2 mice, N = 15; K6PC-5-treated R6/2 mice, N = 15. (E) Mouse body weight during the entire period of the treatment. Vehicle-treated WT mice, N = 8; K6PC-5-treated WT mice, N = 8; vehicle-treated R6/2 mice, N = 12; K6PC-5-treated R6/2 mice, N = 12. Values are represented as mean ± SD. #p < 0.05; ##p < 0.01; ###p < 0.0001; ####p < 0.0001 (vehicle-treated WT vs. vehicle-treated R6/2 mice). $p < 0.05; $$$$p < 0.0001 (vehicle-treated WT vs. K6PC-5-treated R6/2 mice). **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001 (K6PC-5-treated WT vs. vehicle-treated R6/2 mice). @p < 0.05; @@@p < 0.001; @@@@p < 0.0001 (K6PC-5-treated WT vs. K6PC-5-treated R6/2 mice). £p < 0.05; ££p < 0.01; ££££p < 0.0001 (vehicle-treated R6/2 vs. K6PC-5-treated R6/2 mice; Two-Way ANOVA with Bonferroni post-test). (F) Kaplan Maier curve of survival HD. Vehicle-treated R6/2 mice, N = 6; K6PC-5-treated R6/2 mice, N = 6. **p < 0.01. Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test.