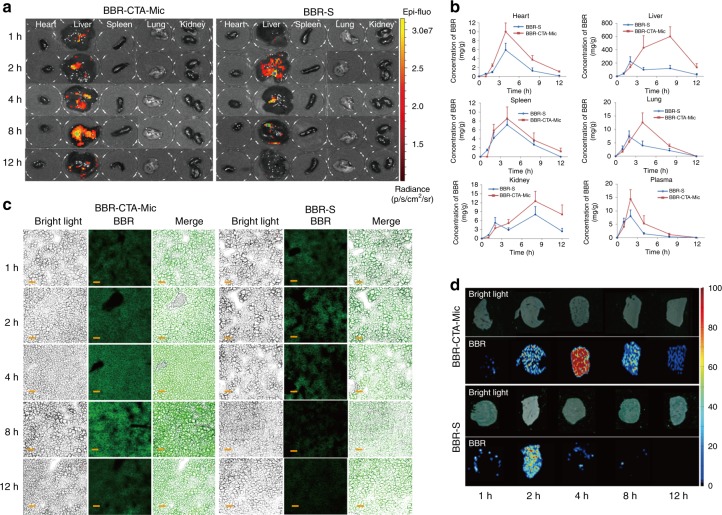
Fig. 3.
Bio-distribution Evaluation. C57BL/6J mice were administered with BBR-S or BBR-CTA-Mic (50 mg kg−1 of BBR) via gavage injection. a At each predetermined time point, a group of five mice for each formulation were euthanized and blood (0.5 mL) were obtained from posterior orbital venous plexus to a heparinized tube and major organs (heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney) were harvested. Major organs were imaged using the IVIS imaging system at excitation/emissio n = 465/540 nm. (Heart, liver, spleen, lung, and kidney, from left to right). b Quantitative analysis of the distribution of BBR in C57BL/6J mice at different time points achieved via LC/MS/MS. (n = 5, mean ± SEM). Liver-focused evaluation was applied to further assay the hepatic cell accumulation of BBR in BBR-S or BBR-CTA-Mic group. The cryostat sections of liver sample were prepared by cutting the liver tissue into 4 μm. c Liver cell accumulation of BBR was visualized using CLSM LSM710 (Carl Zeiss, Germany) Ex = 365 nm; Em = 480 nm. d Liver accumulation of BBR was tested using ambient mass spectrometry imaging method. The experiments were performed on an air-flow-assisted desorption electrospray ionization (AFADESI)-MSI platform equipped with a Q-Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Scale bars, 50 μm (c)