FIGURE 1.
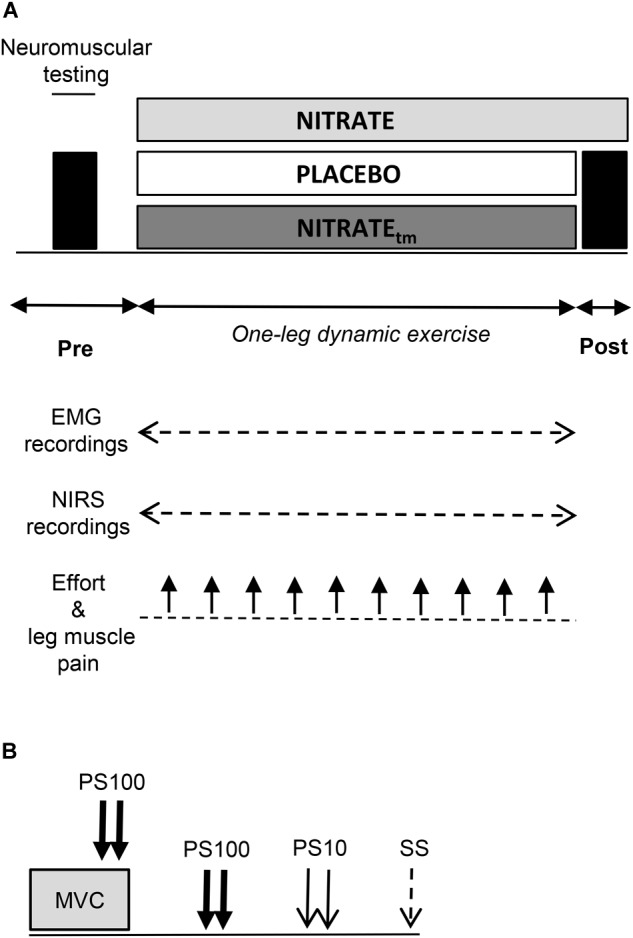
(A) Illustration of the experimental design. A time-to-exhaustion test of the knee extensors was performed after 5 days of dietary nitrate (NITRATE) and PLACEBO supplementation. Neuromuscular function of the quadriceps muscle was assessed before and immediately after both PLACEBO and time-matched dietary nitrate condition (NITRATEtm). Effort perception and leg muscle pain were recorded every min during exercise. Electromyography (EMG) and near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) data were continuously recorded during exercise. (B) The neuromuscular testing procedure comprised isometric MVC of the knee extensors combined with electrical stimulation to assess maximal voluntary torque (MVT), voluntary activation (via the interpolated twitch technique), and quadriceps twitch torques in response to paired electrical stimuli at 100 Hz (PS100) and at 10 Hz (PS10) as well as single stimuli (SS). A representative torque-time curve of the neuromuscular assessment procedure can be found in a previous publication from our group (Husmann et al., 2018).
