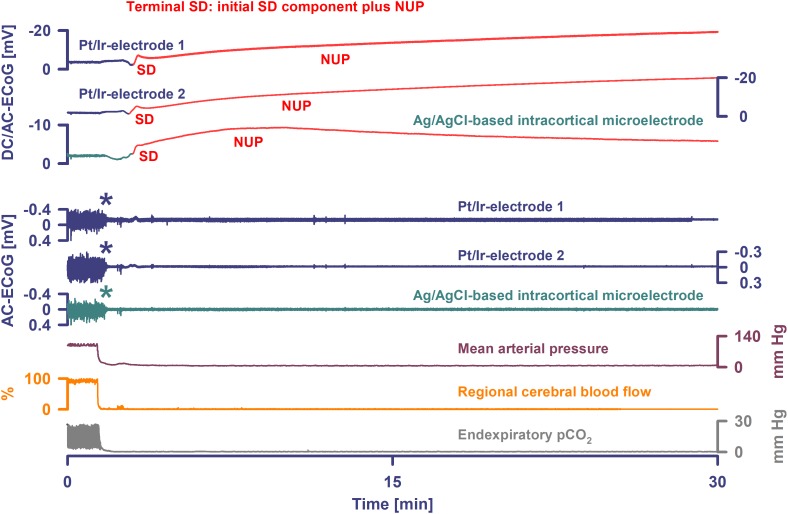
FIGURE 4.
Terminal SD in the wake of circulatory arrest. Sudden circulatory arrest was induced in this rat by injection of 10 ml of air into the heart via the femoral vein. MAP fell rapidly from 99 to 6 mmHg and respiratory fluctuations of expiratory pCO2 ceased within 18 s; non-spreading depression caused isoelectricity within 26 s (asterisks) and terminal SD started after 98 s. Terminal SD showed an initial and a late negative DC component similar to human recordings (Dreier et al., 2018b). Whereas the initial one is the actual SD component, the late one is termed the NUP.