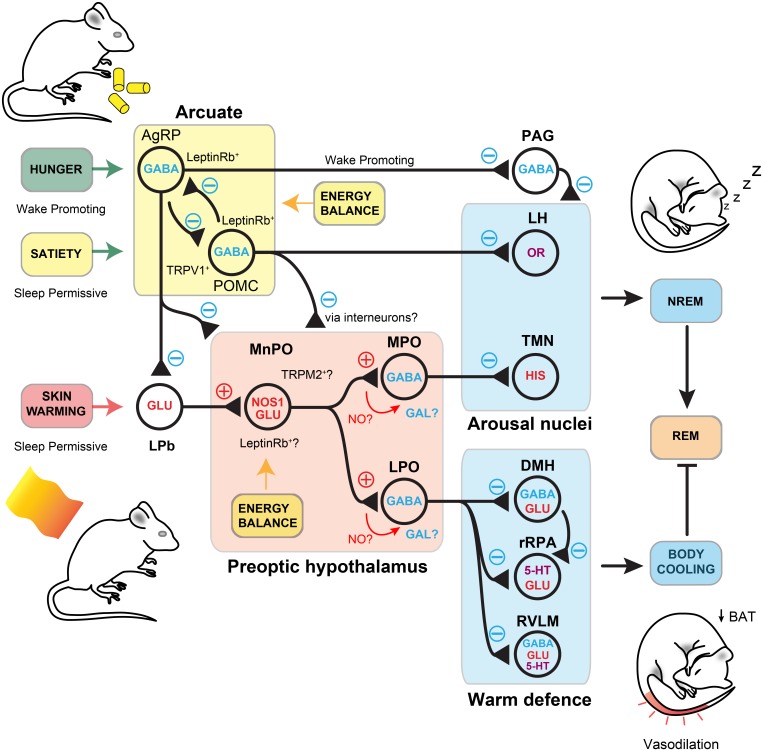
FIGURE 4.
Signal integration in the preoptic hypothalamus. Warmth on the skin stimulates sensory inputs, through the LPb, to preoptic nitrergic-glutamatergic neurons that initiate simultaneous NREM and body cooling. This maybe through activation of separate GABAergic neurons for sleep and hypothermia in the MPO and LPO, but they may also activate galinergic-GABAergic neurons to initiate sleep and body cooling. The synaptic role of NO is unknown in these circuits but potential sites are labelled. NREM is initiated by inhibition of arousal nuclei, including the TMN and the LH. Others are likely to be involved. Body cooling is facilitated by activation of DMH and inhibition of rRPA neurons to induce vasodilation and downregulation of BAT thermogenesis. Inputs to the lateral parabrachial and the preoptic area are modulated by AgRP neuron-mediate inhibition from the arcuate. These detect hunger and put a break on NREM. Satiety induces activation of POMC neurons, that also express TRPV1, are permissive for NREM and induce local inhibition of AgRP neurons. Nitrergic-glutamate neurons may respond to leptin through the leptin Rb, as do AgRP and POMC neurons. They, or a separate local population, may also respond to changes in brain temperature through the TRPM2 ion channel. NO, nitric oxide; NOS1, nitric oxide synthase-1; PO, preoptic area; LPO, lateral preoptic area; vPAG, ventral periaqueductal grey; TMN, tuberomammillary nucleus; ARC, arcuate nucleus; LPb, lateral parabrachial; BAT, brown adipose tissue; AgRP, agouti-related peptide; POMC, pro-opiomelanocortin; DMH, dorsal medial hypothalamus; rRPA, rostral raphe pallidus; RVLM, rostral ventrolateral medulla; TRPM2, transient receptor potential cation channel; TRPV1, transient receptor potential cation channel vallinoid-1; GAL, Galanin (Leshan et al., 2012; Weber and Dan, 2016; Yu et al., 2016; Goldstein et al., 2018; Harding et al., 2018; Jeong et al., 2018; Tan and Knight, 2018; Yu et al., 2019).