FIGURE 2.
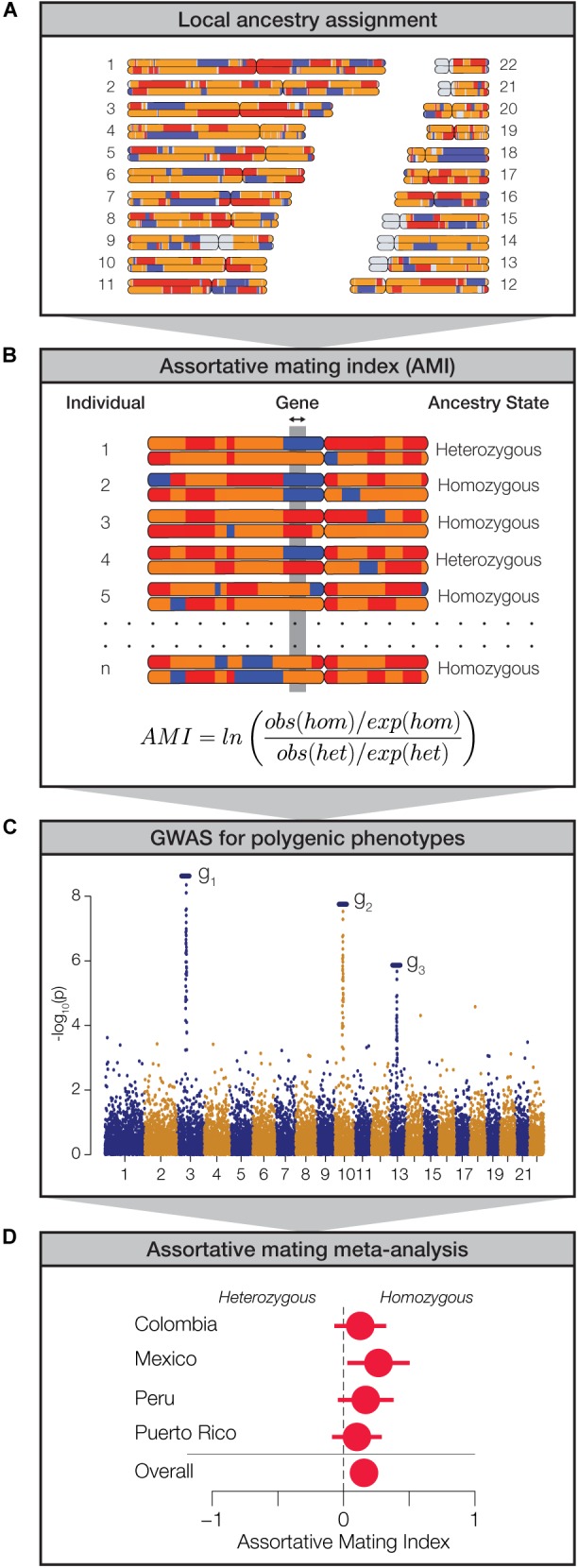
Approach used to measure assortative mating on local ancestry. (A) Local ancestry is assigned for specific haplotypes across the genome: African (blue), European (orange), and Native American (red). (B) Within individual genomes, genes are characterized as homozygous or heterozygous for local ancestry. For any given population, at each gene locus, the assortative mating index (AMI) is computed from the observed and expected counts of homozygous and heterozygous gene pairs. (C) Data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) are used to evaluate polygenic phenotypes. (D) Meta-analysis of AMI values is used to evaluate the significance of ancestry-based assortative mating for polygenic phenotypes.
