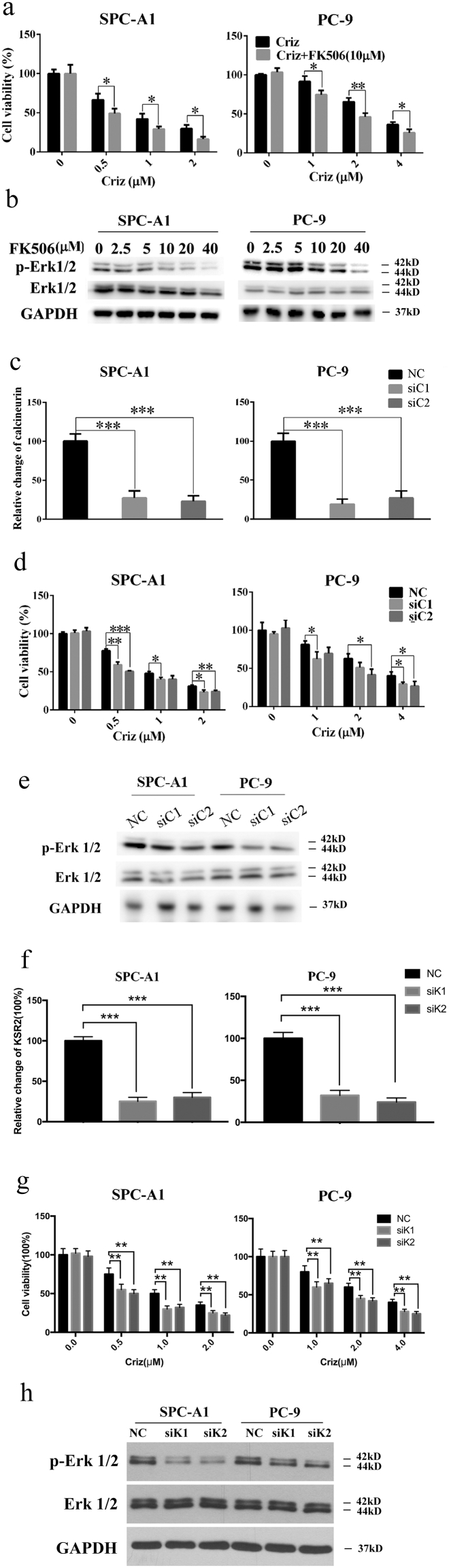
Fig. 7.
Inhibition of calcineurin sensitizes NSCLC cells to crizotinib treatment. (a) SPC-A1 and PC-9 cells were treated with crizotinib in the presence or absence of FK506 for 48 h, after which the viability was determined by MTS assay. (b) Cells were treated with FK506 for 72 h, after which the expression of phosphorylated and total Erk1/2 was examined by immunoblotting. (c) After transfection with siRNA against calcineurin (siC1 and siC2) or scramble siRNA (NC) for 72 h, the mRNA level of calcineurin was quantified by RT-PCR. (d and e) After transfection with siRNA against calcineurin, cells were treated with crizotinib for 48 h, after which the cell viability was determined by MTS assay (d) and the expression of phosphorylated and total Erk1/2 was examined by immunoblotting (e). (f) After transfection with siRNA against KSR2 (siK1 and siK2) or scramble siRNA (NC) for 72 h, the mRNA level of calcineurin was quantified by RT-PCR. (g and h) After transfection with siRNA against KSR2, cells were treated with crizotinib for 48 h, after which the cell viability was determined by MTS assay (g) and the expression of phosphorylated and total Erk1/2 was examined by immunoblotting (h). *P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001 compared with control. Values were presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments and compared using student's t-test.