Figure 1.
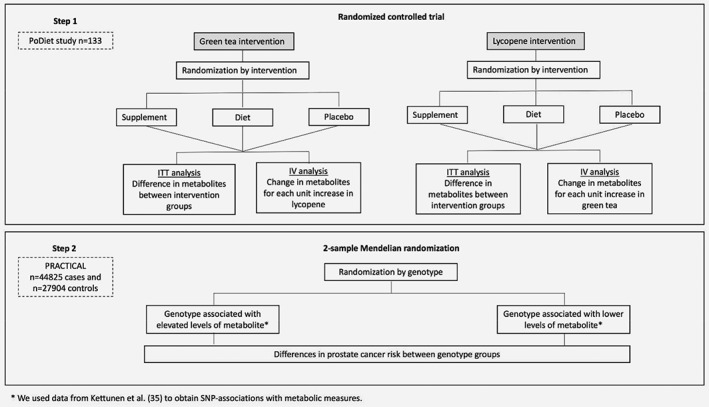
Analysis steps for investigating the effects of lycopene and green tea on serum metabolome of men at risk of prostate cancer, and the causal role of altered metabolic traits on prostate cancer risk. We conducted 2 analyses. In stage one, relationships between metabolic measures and lycopene or green tea randomisation arms were tested using an intention‐to‐treat analyses. In stage two, we used GWAS summary statistics from Kettunen et al to identify genetic variants that could be used as instrumental variables for the effects of metabolites on prostate cancer risk. Data on the association of these genetic variants with prostate cancer risk were obtained from the PRACTICAL consortium (44,825 prostate cancer cases and 27,904 controls of European ancestry). Data on the association of genetic variants with metabolite levels and with prostate cancer risk were combined to estimate the influence of metabolites on prostate cancer risk. ITT, intention‐to treat; IV, instrumental variable.
