Figure 6.
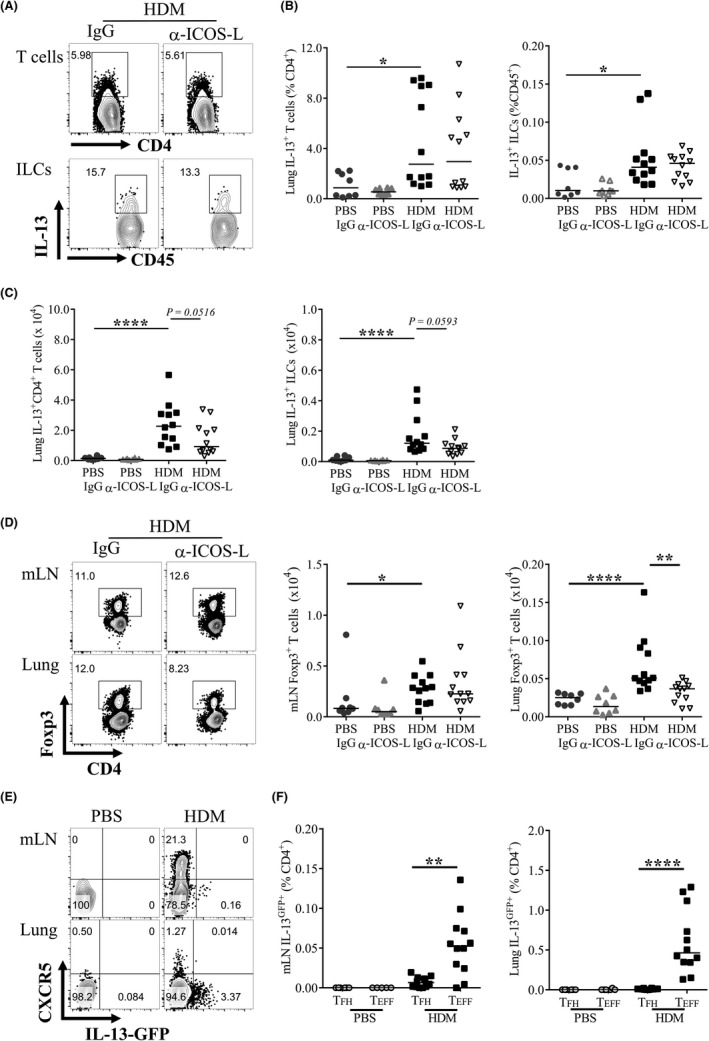
IL‐13+ CD4+ T cells and ILCs are not directly targeted by ICOS‐L blockade. A‐B, Adult female BALB/c mice were exposed to either 25 μg house dust mite (HDM) or 25 μL phosphate‐buffered saline (PBS), three times a week for up to 5 weeks. From the start of week 4, mice were also administered 150 μg anti‐ICOS‐L (α‐ICOS‐L) or isotype control (IgG) antibody (i.p) three times a week. Mice were culled at the end of week 5. Flow cytometry was used to determine the frequency of lung cellular populations. A, Representative gating of IL‐13+ CD4+ T cells and IL‐13+ ILC2s following HDM and IgG or α‐ICOS‐L treatment. Data are quantified for all groups. B, Proportions of lung IL‐13+ T cells and ILCs. C, Numbers of lung IL‐13+ T cells and ILCs. Data are pooled from two independent experiments, n = 8 for PBS‐treated groups, n = 12 for HDM‐treated groups. D, Representative flow cytometry of Foxp3+ CD4+ cells in allergen‐treated mice given IgG or α‐ICOS‐L. Pre‐gated on CD4+ CD3+ lymphocytes. The number of Foxp3+ CD4+ T cells is quantified for all groups, E‐F, Adult female IL‐13GFP reporter mice were exposed (i.n) to 25 μg HDM or 25 μL PBS, three times a week for 3 weeks. Flow cytometry was used to determine the frequency of IL‐13GFP cells. E, Representative flow plots of CXCR5+ T cells and IL‐13‐GFP + cells in PBS and HDM‐treated animals, pre‐gated on CD4+ CD3+ CD44hi CD62L− lymphocytes. F, Quantification of mLN and lung IL‐13GFP + TFH (CXCR5+ PD1+ CD4+ CD44hi CD62L−) and TEFF cells (CXCR5− CD4+ CD44hi CD62L−). Statistical significance was determined using a Mann‐Whitney U test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data are pooled from two independent experiments, n = 6 for PBS‐treated groups, n = 12 for HDM‐treated groups
