Figure 3.
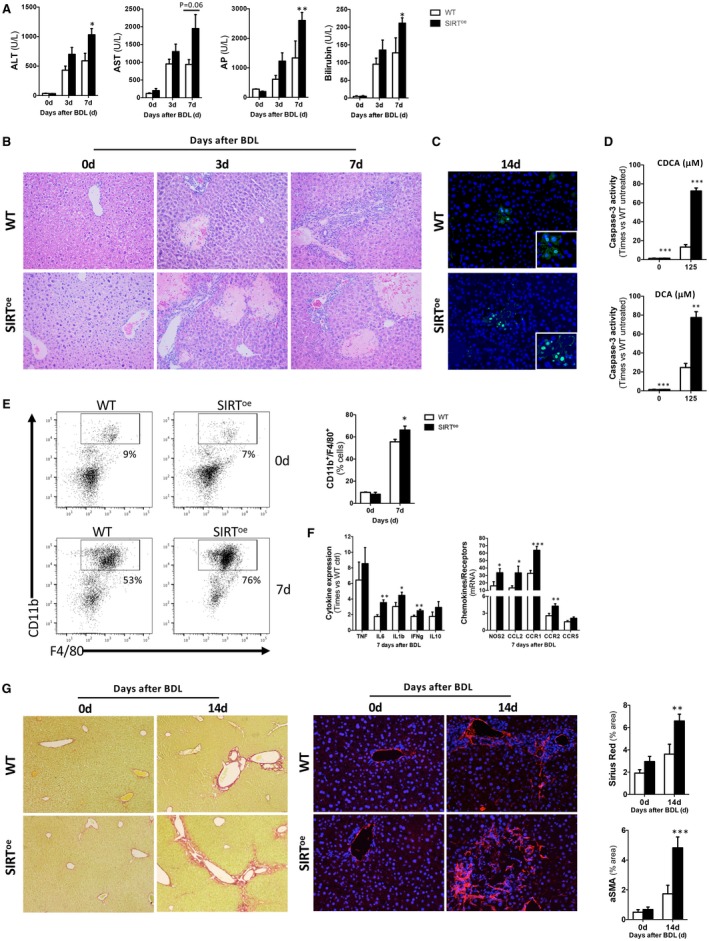
Overexpression of SIRT1 leads to increased parenchymal injury and fibrogenesis in mice after BDL. (A) Profiles of blood liver injury markers detected in WT and SIRToe animals and (B) H&E staining of liver sections from WT and SIRToe animals after BDL showing profuse liver damage in SIRToe mice. (C) TUNEL assay on liver sections showing increased presence of apoptotic hepatocytes in SIRToe mice compared to WT after BDL. (D) Caspase‐3 activity was determined in primary hepatocytes isolated from WT and SIRToe mice and cultured in the presence of CDCA and DCA. (E) FACS analysis on liver isolated immune cells and (F) qPCR analyses of inflammation markers showed increased presence of macrophages and increased proinflammatory response in SIRToe mice. (G) Liver fibrogenesis was characterized by Sirius Red staining on liver sections (left panels) and αSMA IHC (right panels) from mice after BDL, followed by morphometric quantification using Frida software expressed in % of positive staining per power field (ppf). Images are representative of n ≥ 5 animals/time point; values are mean ± SEM; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0 .001 (WT vs. SIRToe). Abbreviations: ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AP, alkaline phosphatase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase.
