Figure 6.
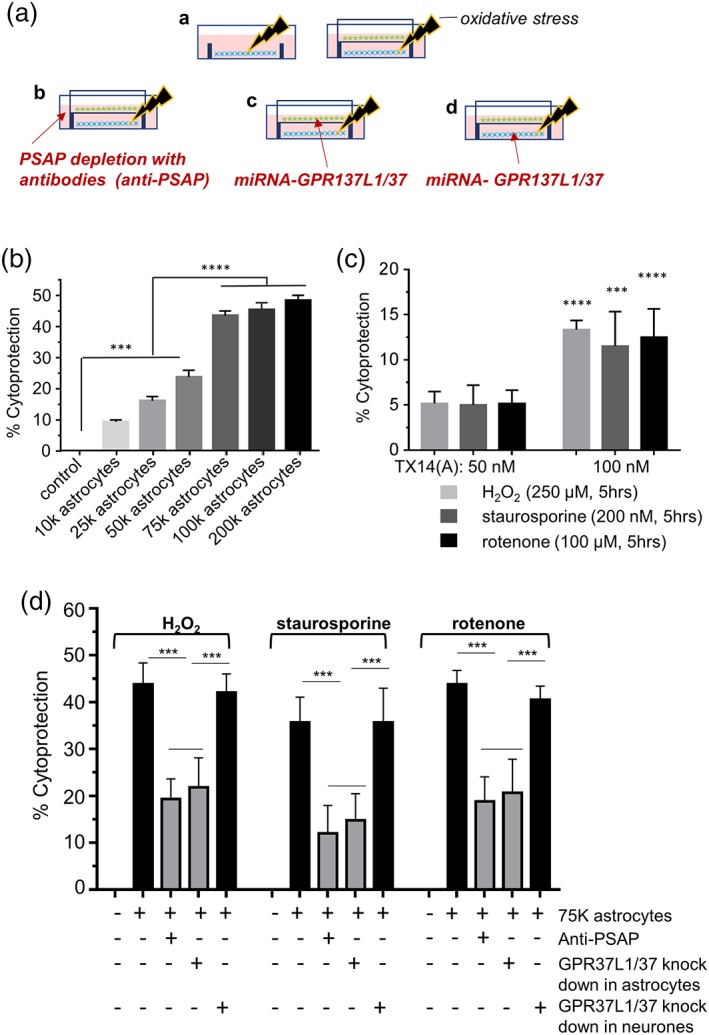
Co‐cultured astrocytes protect cortical neurons against oxidative toxicity partially through GPR37L1/GPR37 signaling in astrocytes. (a) Experimental design: (A—stressed neurons (blue) in absence or presence of astrocytes (green) on a culture insert; B—depletion of PSAP from the media with anti‐PSAP antibodies; C—GPR37L1 and GPR37 knock‐down in astrocytes co‐cultured with neurons; D—GPR37L1 and GPR37 knock‐down in neurons in the co‐culture system. Neurons were treated with H2O2 (250 μM) for 1 hr, or staurosporine (100 nM) or rotenone (50 μM) for 2 hr. Stressors were then removed and inserts with astrocytes were introduced. LDH assay was carried out 24 hr later. (b) Astrocytes protect cortical neurons against H2O2‐induced stress, the effect saturates at ~75 k astrocytes per co‐culture (n = 5, triplicates, ***p < .001 vs. control [no astrocytes insert], ****p < .0001 vs. groups with less than 50 k astrocytes, one‐way ANOVA with Tukey's post hoc analysis). (c) TX14(A) has a weak protective effect on neurons against oxidative stress (n = 6, triplicates, ***p < .001, ****p < .0001 vs. 50 nM TX14(A) group (effect of 50 nM is not significant, one‐way ANOVA with Bonferoni's post hoc analysis). D: PSAP depletion or GPR37L1/GPR37 knock‐down selectively in astrocytes significantly attenuates the protective effect of astrocytes on neurons pre‐exposed to oxidative stressors (n = 6, triplicates, ***p < .001 vs. indicated group, one‐way ANOVA with Turkey's post hoc analysis) [Color figure can be viewed at wileyonlinelibrary.com]
