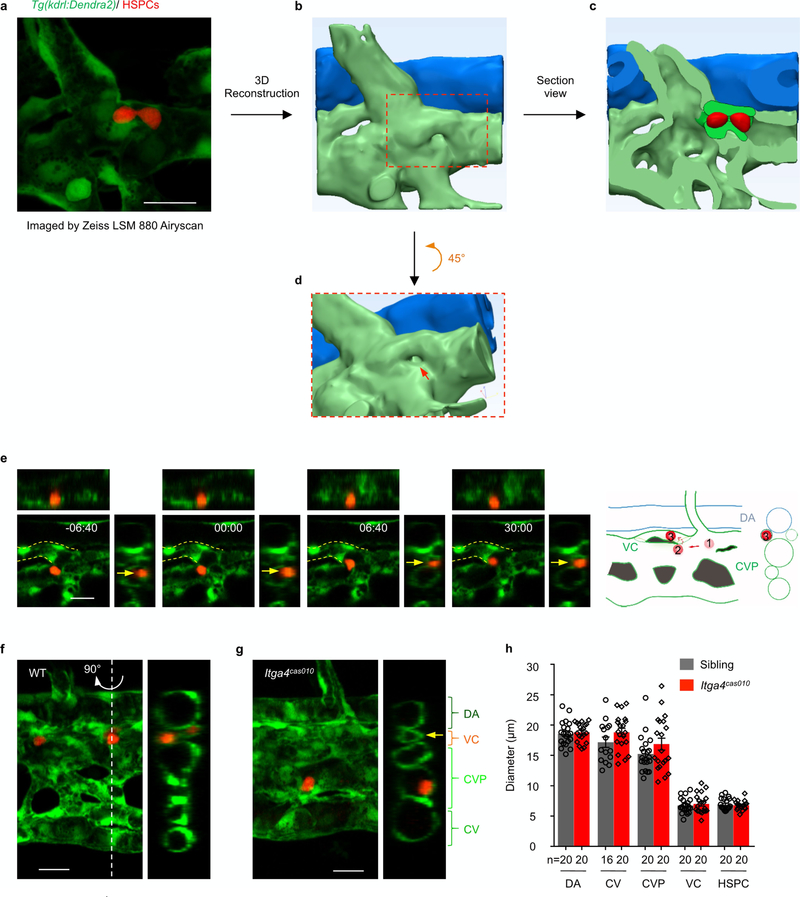
Extended Data Fig. 6 |. The representative high-resolution vascular structure and HSPC in the retention hotspot.
a, The original fluorescent image of the vessel surrounding HSPCs in the retention hotspot was captured by an LSM880 microscope equipped with Airyscan function and processed by 3D reconstruction (see Supplementary Video 4). b, 3D reconstruction of a. c, Section view of the caudal vein plexus and capillary. d, The 45° rotation view of the red frame in b. e, Time-lapse imaging (left) and scheme graph (right) show how HSPC retention occurs. HSPCs initially came into the venous plexus and then entered the venous capillary for long-term retention. f–h, Images (f, g) and statistical analysis (h) show that the diameter of various vessels in the CHT in itga4cas010 mutants (g) is similar to that in the wild-type siblings (f) at 54 h.p.f. The inner diameter of venous capillaries, but not other vessels, is close to the diameter of HSPCs. DA: P = 0.73, t = 0.35, df = 19; CV: P = 0.14, t = 1.52, df = 33; CVP: P = 0.17, t = 1.41, df = 19; VC: P = 0.63, t = 0.49, df = 19; HSPC: P = 0.67, t = 0.44, df = 19. Scale bar, 20 μm.