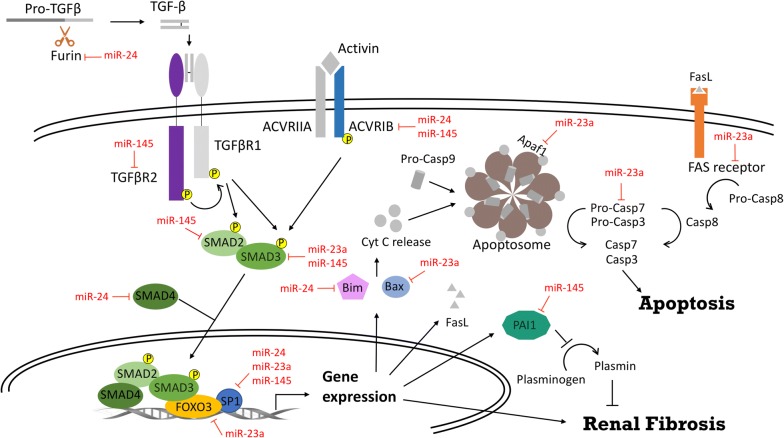
Fig. 4.
Schematic overview for the roles of miR-24, miR-23a and miR-145 in TGF-β signaling in AKI. The proteolytic activity of Furin is required for the maturation of TGF-β. After binding with mature TGF-β, TGFβR2 phosphorylates TGFβR1 and induces canonical SMAD2/3 signaling. Phosphorylated SMAD2/3 interacts with SMAD4, and this complex translocates into the nucleus and associates with transcription factors (FOXO3 and SP1) to regulate target gene expression. The pro-apoptotic factors, Bim and Bax, are induced by TGF-β-SMADs signaling to cooperatively trigger the release of Cyt C from mitochondria. Cyt C, Pro-Casp9 and Apaf1 form the apoptosome, which can initiate intrinsic apoptosis through the caspase 9-mediated cleavage of caspase 3/7. FasL is transactivated by the canonical TGF-β pathway, binds to Fas receptor, and enhances extrinsic apoptosis by autolysis of Pro-Casp8. Activated caspase 8 also converts caspase 3/7 into active enzymes and induces cell death. SMAD2/3 transactivates pro-fibrotic genes that are directly involved in extracellular matrix deposition. PAI1 is also activated via the TGF-β-SMADs pathway; activated PAI1 reduces the production of plasmin and protects fibrin from degradation, thereby promoting tissue fibrosis. The experimentally confirmed targets of miR-24, miR-23a and miR-145 are marked. AKI acute kidney injury, Apaf1 apoptotic protease activating factor 1, Cyt C cytochrome C, FasL Fas ligand, FOXO3 forkhead box O3, PAI1 plasminogen activator inhibitor-1, Pro-Casp8 pro-caspase 8, Pro-Casp9 pro-caspase 9, TGF-β transforming growth factor beta, TGFBR1 transforming growth factor, beta receptor I, TGFBR2 transforming growth factor, beta receptor II, SP1 specificity protein 1