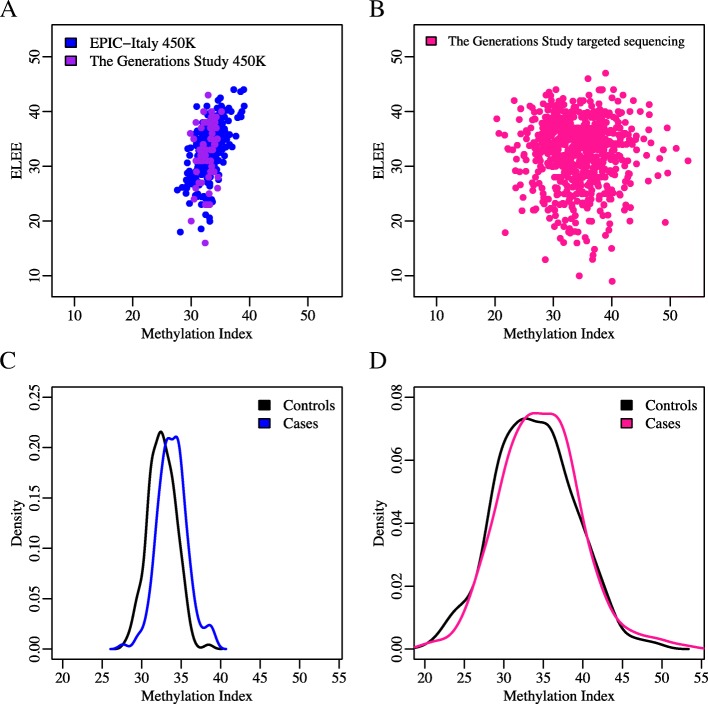
Fig. 2.
The MI is associated with breast cancer risk. The MI was developed in combined HM450K data from EPIC-Italy (dataset 2, n = 237) and the Generations Study (dataset 3, n = 65) using ridge regression. The correlation between the MI and ELEE and the association between the MI and breast cancer risk were evaluated. a The correlations between the MI and ELEE in the development of HM450K data were as follows: r = 0.60 and P = 6 × 10−25 for EPIC-Italy and r = 0.27 and P = 0.027 for the Generations Study b The MI and ELEE were not correlated in the Generations Study targeted sequencing data (r =− 0.04, P = 0.340). c Density plot of the MI values in controls and cases in EPIC-Italy HM450K data. The MI was significantly associated with breast cancer risk in EPIC-Italy (n = 162 pairs, OR = 1.51, 95% CI 1.26–1.82, P = 1 × 10−5). d Density plot of the MI values in controls and cases in the Generations Study targeted sequencing data. The MI was significantly associated with breast cancer risk in the Generations Study (n = 339 pairs, OR = 1.04, 95% CI 1.01–1.08, P = 0.022). ORs were adjusted for age, BMI, alcohol consumption, and smoking duration (all variables reported at recruitment) and WBC composition