Figure 6.
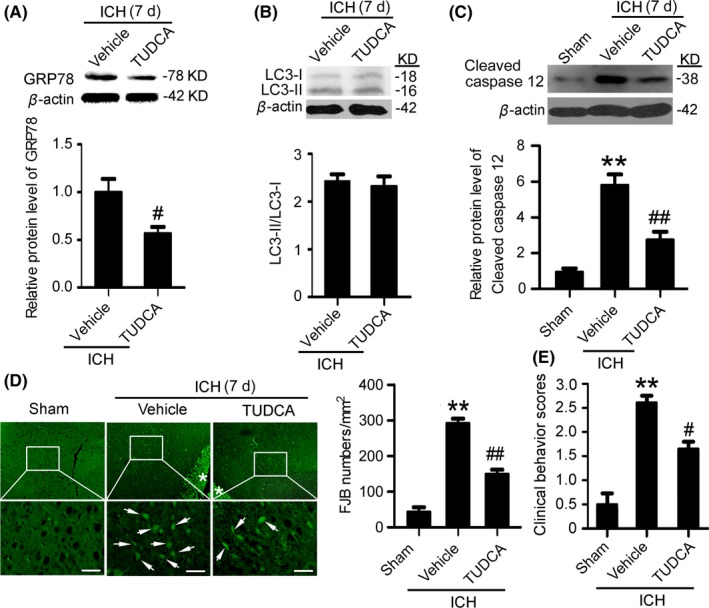
Inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress mitigates secondary brain injury (SBI) at 7 d after intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH). (A) GRP78 protein levels and statistics in perihematoma tissues of the rat ICH model determined by Western blots. (B) The conversion of LC3‐I to LC3‐II and statistics in perihematoma tissues of the rat ICH model determined by Western blots. (C) Cleaved‐caspase 12 protein levels and statistics in perihematoma tissues of the rat ICH model determined by Western blots. (D) Fluoro‐Jade B (FJB) staining shows neuronal degradation (green). Arrows point to FJB‐positive cells. Asterisks indicate hematoma location. Bar=64 μm. FJB‐positive cells/mm2 in perihematomal brain were shown. (E) Clinical Behavior Scores. In (A, B, C, D and E), bars represent mean±SEM, **P<.01 compared with the sham group and #P<.05, ##P<.01 compared with the vehicle group, n=18. LC3, microtubule‐associated protein light‐chain 3; GRP78, glucose‐regulated protein 78; TUDCA, tauroursodeoxycholic acid
