Figure 6.
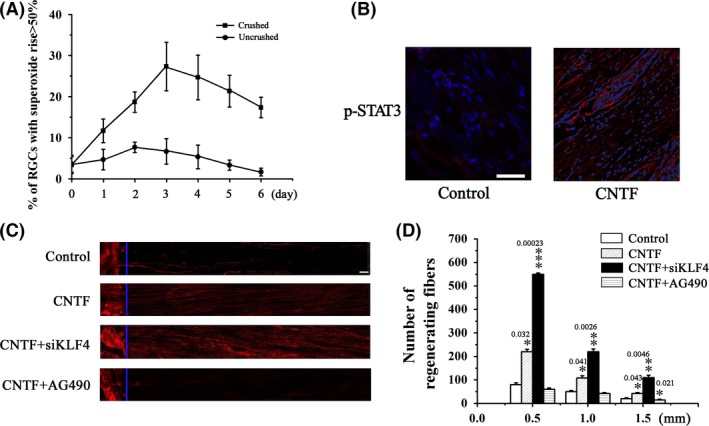
Axotomy of RGCs by optic nerve crush induces oxidative stress. (A) RGCs were dissociated from the crushed retina at the indicated time postinjury. Superoxide levels were determined using HEt staining 1 h after dissociation. RGCs dissociated from the uninjured retina were used as control. n = 5. (B) CNTF (1 μL of 10 μg/mL) or vehicle was intravitreally injected immediately after injury and 3 days later. Retina was dissected 24 h after the second injection and p‐STAT3 was detected by immunohistochemical analysis. (C, D) Immediately following the injury, CNTF (1 μL of 10 μg/mL), CNTF (1 μL of 10 μg/mL) in combination with siKLF4 (100 μL of 108 TU/mL), CNTF (1 μL of 10 μg/mL) in combination with AG490 (30 μg), or vehicle alone was intravitreally injected. Animals were sacrificed on day 21. Optic nerves were dissected from the injured eye. Axon regeneration was assessed by immunohistochemical analysis based on GAP43 staining. (C) Representative fluorescence images of optic fibers. Scale = 100 μm. (D) Numbers of regenerating axons at the indicated distance distal to the crush sites. n = 5, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs. control.
