Figure 1.
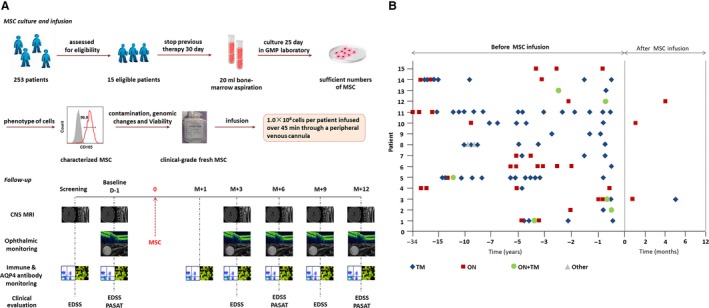
Study design and effects of MSC infusion on relapse of NMOSD. (A) Study design: Fifteen eligible patients with NMOSD were enrolled. Prior to bone marrow aspiration, all treatments with corticosteroids and other systemic immunosuppression therapies were discontinued for 30 days. Bone marrow cell aspirates (20 mL) were obtained while patients were under local anesthesia from the posterior iliac crest. Following current good manufacturing practices, mononuclear bone marrow cells were isolated by Percoll (1.073 g/mL) centrifugation and allowed to adhere to a flask for 72 h in low‐glucose Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium (GibcoInvitrogen), and the culture medium was changed every 3 days. The phenotype of the cells was assessed by flow cytometry to confirm the expression of CD73, CD90, and CD105 surface molecules (>95%) and absence of CD34, CD45, CD14, and CD3 (<2%), and the ability of the cells to differentiate into adipocytes and osteocytes in culture was confirmed in vitro following the 2006 International Society of Cellular Therapy's criteria.25 At 70–80% confluence, cells were detached and re‐plated at 1 × 106/175 cm2 culture to process for infusion. Cell viability was determined by trypan blue staining at the end of the harvest. Viability was greater than 95% for infusion and tested negative for endotoxin, hepatitis C virus, hepatitis B virus, HIV, syphilis, fungi, Mycoplasma species, and Chlamydia before infusion. G‐banding karyotype analysis was performed to confirm the absence of chromosomal aberrations in the final cellular product.26 After MSCs were characterized in accordance with the International Society of Cellular Therapy (ISCT) recommendations,25 108 MSC of 5 × 105 cells/mL were transferred into 200‐mL syringes for intravenous infusion over a 45‐minute time period for each patient. All participants were assessed at 1 day (D‐1, baseline) before treatment and at 1 month (M + 1), 3 months (M + 3), 6 months (M + 6), 9 months (M + 9), and 12 months (M + 12) after treatment. Assessments included clinical assessment (Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) and Paced Auditory Serial Addition Test [PASAT]); optical nerve, brain, and spinal cord MRI; visual evoked potential, optical coherence tomography (OCT), and ophthalmological assessments (visual acuity, visual field); serum anti‐AQP4 antibody concentrations; and lymphocyte phenotyping. (B) Frequency of relapses before and after mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) infusion, TM = transverse myelitis, ON = optic neuritis.
