Figure 3.
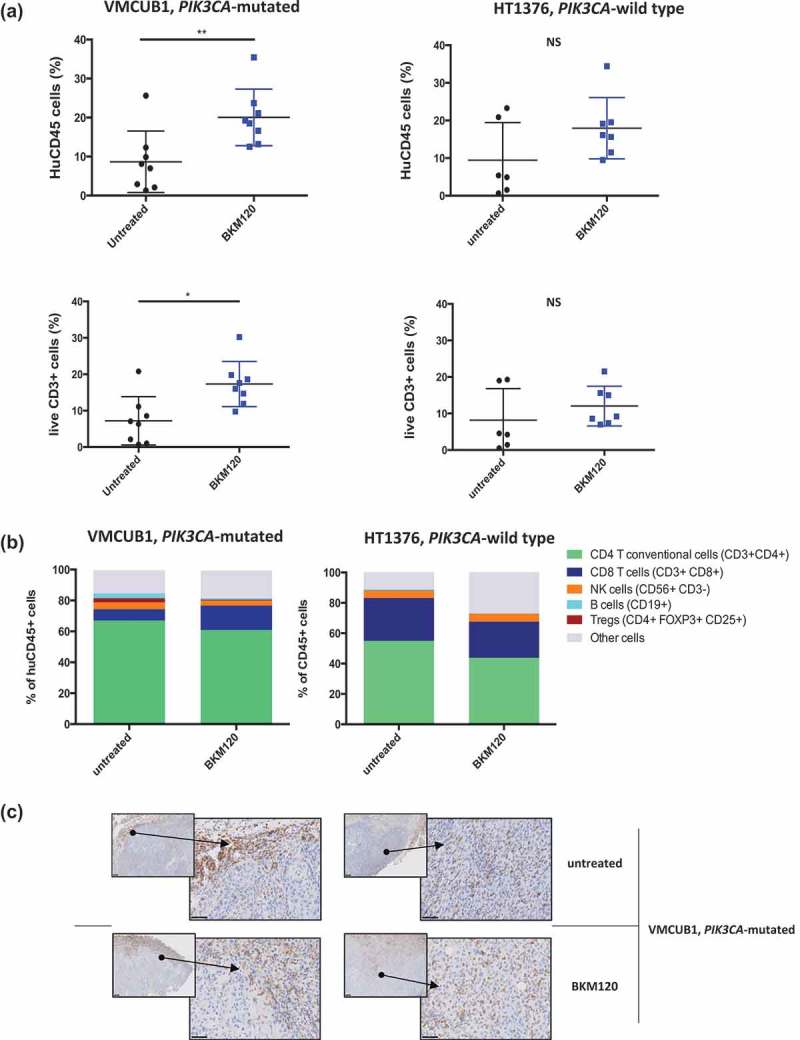
Effect of BKM120 treatment on the tumor immune infiltrate of VMCUB1, PIK3CA-mutated, and HT1376, PIK3CA-wild type human bladder tumors in humanized mice.
Humanized mice were treated as in Figure 2 and tumors were analyzed at day 25.a. FACS analysis showing the proportion of total HuCD45+ and CD3+ T cells infiltrating the tumor, among live cells. Left panels: PIK3CA-mutated VMCUB1 tumors (N = 8 in each group); right panels: PIK3CA-wild type HT1376 tumors (N = 6 in the untreated group and N = 7 in the BKM120 group).b. Proportion of the indicated immune cell subsets among tumor-infiltrating HuCD45+ cells. Results shown are from one representative experiment out of two with similar results. Statistical significance was calculated using the Mann–Whitney test. NS, not significant; *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01.C. VMCUB1 PIK3CA-mutated tumors from untreated and BKM120-treated mice were characterized by IHC for human infiltrate (HuCD45). Representative IHC stainings of two mice per indicated group are shown with two different magnifications: smaller square, x50; larger square, x400.
