Figure 6.
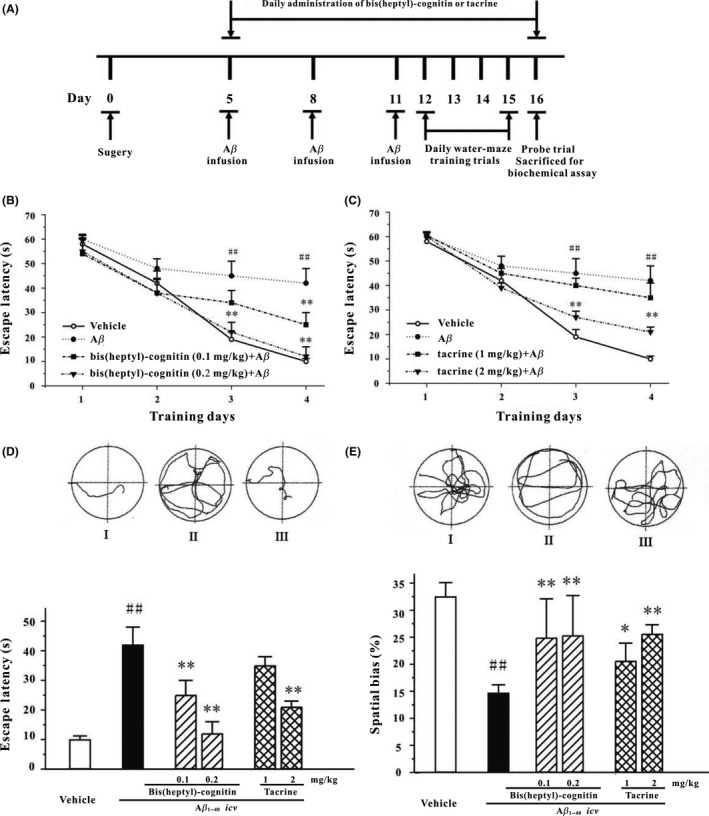
B7C potently reverses the memory deficits induced by icv infusion of Aβ1–40 in rats. (A) The schedules of animal experiments. (B, C) Mean latency to escape from the water onto the hidden platform. Each rat was subjected to two trials per day for 4 consecutive days. (D) Upper: typical swimming‐tracking path of vehicle control (I), groups of rats treated with Aβ1–40 (II), and groups of rats treated with 0.2 mg/kg B7C plus Aβ1–40 (III), on the fourth training day in Morris water maze. Lower: mean latency to escape from the water onto the hidden platform in fourth training day. (E) Upper: typical swimming‐tracking path of vehicle control (I), groups of rats treated with Aβ1–40 (II), and groups of rats treated with 0.2 mg/kg B7C plus Aβ1–40 (III), on the fifth probe trial day in Morris water maze. Lower: the swum distance in the target quadrant (southeast, in which the platform had been placed during the training phase) in the probe trial (swimming 60 s without platform). Data represent means ± SEM. ## P < 0.01 vs. vehicle group; **P < 0.01 vs. Aβ1–40‐treated group.
