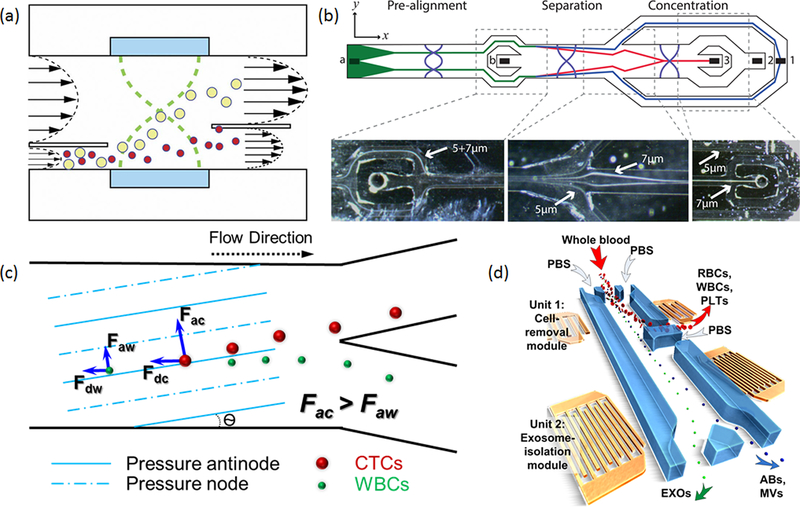
Figure 3.
(a) Typical setup of an acoustofluidic, half-wavelength particle separator. Reproduced with permission from ref 54. Copyright 2012 the Royal Society of Chemistry. (b) An integrated acoustic separator with prefocusing, separation, and concentration units. Reproduced with permission from ref 55. Copyright 2015 American Chemical Society. (c) Working mechanism for taSSAW-based cell separation. Reproduced with permission from ref 22. Copyright 2015 the National Academy of Science. (d) Two-stage separation device using taSSAWs for the isolation of exosomes from whole blood. Two pairs of IDTs with different wavelengths are used to separate cells and vesicles, respectively. Abbreviations: RBCs, red blood cells; WBCs, white blood cells; PLTs, platelets; EXOs, exosomes; Abs, apoptotic bodies; MVs, microvesicles. Reproduced with permission from ref 66. Copyright 2017 the National Academy of Science.