Figure 4.
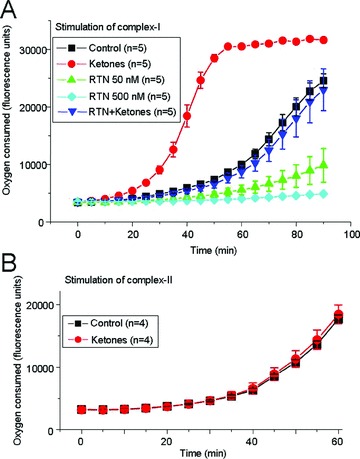
The effects of rotenone and ketones on complex I‐driven mitochondrial respiration. (A) The amount of oxygen consumed by isolated mitochondria was estimated using the Oxygen Biosensory System (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA, USA) in the presence of rotenone alone or in combination with ketones (1 mM acetoacetate plus 1 mM DL‐β‐hydroxybutyrate). Complex I was activated with 10 mM glutamate, 10 mM malate and 1 mM ADP. Oxygen consumption was clearly decreased by 50 nM rotenone (green), and 500 nM rotenone completely blocked mitochondrial respiration (cyan). In contrast, ketones enhanced complex I‐driven mitochondrial respiration and prevented the inhibitory effects of rotenone. The differences between the rotenone and rotenone plus ketones groups were statistically significant (n = 5 animals in each experimental group; ANOVA, P < 0.05). (B) Ketones did not affect mitochondrial respiration driven by the complex II substrate succinate (10 mM) in the presence of ADP (1 mM) and rotenone (1 μM).
