Figure 4.
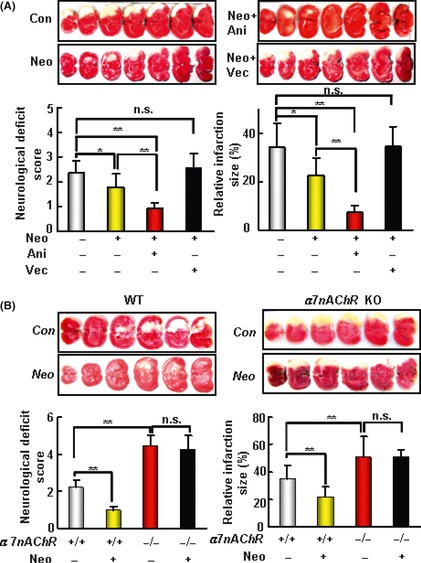
The protective effect of neostigmine (Neo) on acute ischemic cerebral injury induced by middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) depends on nAChR‐α7nAChR. (A) The cerebral protective effect of Neo depends on nAChR. The upper panel shows representative 2‐3‐5‐triphenyltetrazolium‐chloride (TTC)‐stained of seven corresponding coronal brain sections of vehicle control (Con), Neo (40 μg/kg), Neo + anisodamine (Ani, 20 mg/kg), and Neo + vecuronium (Vec, 400 μg/kg) treatment group rats on day 1 after MCAO. (B) The cerebral protective effect of Neo depends on the subunit of nAChR, α7nAChR. The upper panel shows representative TTC‐stained of seven corresponding coronal brain sections of α7nAChR knockout (KO) and WT mice on day 1 after MCAO. Neo (80μg/kg) significantly decreased the infarct size and improved the neurological score in α7nAChR WT mice but not in KO mice. Data are expressed as mean ± SD. Data were analyzed by one‐way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by LSD t‐test.*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. n = 9–12 in each group of A; n = 6–7 in each group of B.
