Figure 1.
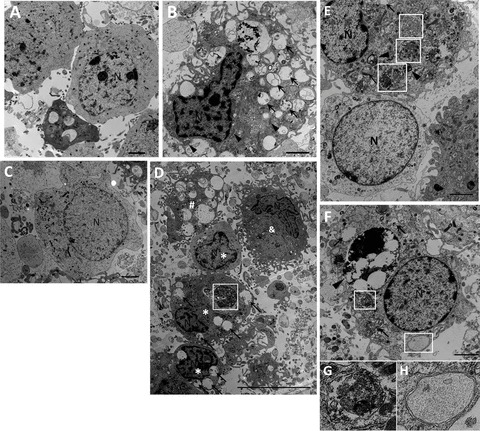
Ultrastructural changes in primary cortical neurons after OGD/RP injury. Primary neurons were subjected to OGD for 6 h then followed by RP for 48 h (C and D) and 72 h (B and E–H) and were fixed for EM examination. Electron microscopy (EM) images showing: Normal appearance of cytoplasm, organelles, and nucleus in control neurons (A). N, nucleus; Ultrastructural features of autophagic cell death were detected in neurons treated by OGD 6 h followed by RP 72 h. Cell shrinkage, nuclear condensation (without fragmentation), loss of cellular organelles, and formation of numerous autophagic vacuoles (black arrows) were shown in the picture (B, D, E, F). Mitochondria also displayed swelling and dilation as indicated by black arrowheads (B). Coexistence of morphological features of normal neurons (C, and lower cell in E), autophagic cell death (*), necrosis (#), and apoptosis (&) can be found in the same group of neurons treated by OGD 6 h followed by RP 48 h (D). White boxes represent autophagosomes; Black arrows represent autophagic vacuoles. Abundant double‐membrane structures and double‐membrane autophagosomes formed in neurons after OGD/RP treatment (D–H, as indicated by White boxes). Lysosomes stained darkened, indicating the activation of lysosomes (as shown by black arrowheads). An autophagosome fused with a lysosome. (E, as indicated by the lowest white box with beside black arrowhead). N = nucleus; Black arrows represent autophagic vacuoles; (G) and (H) showed the enlarged autophagosomes in (F). Scale bars = 2 μm in (A–C, E–F); Scale bar = 10 μm in (D).
