Figure 2.
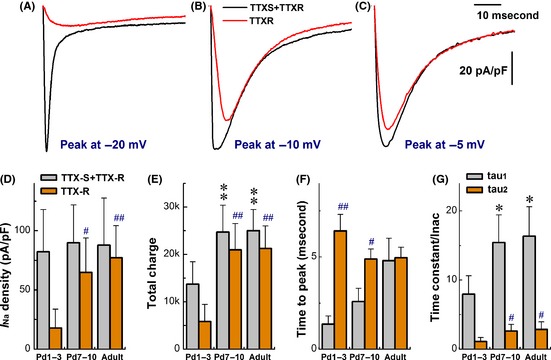
Coordinated change in TTX‐sensitive (TTX‐S) and TTX‐resistant (TTX‐R) Na+ currents of unmyelinated C‐type vagal ganglion neurons (VGNs) and baroreceptor neurons (BRNs) during the development. Voltage‐clamp recordings were performed on unmyelinated VGNs/BRNs isolated from Pd1–3, Pd7–10, and adult rats, respectively. The cell was held at −80 mV and increased from −70 mV to +40 mV with 5 mV increment, 60 ms duration, and 1.0 second step interval. TTX‐R Na+ current was isolated by subtracting the current remaining in the presence of 1.0 μM of TTX from total Na+ currents. (A–C) The representative traces of total Na+ currents (black) and TTX‐R components (red) from Pd‐3, Pd‐9, and adult rats, respectively. (D) Changes in current density. (E) Changes in total charge passing through channels. (F) Changes in time to peaks. (G) Changes in inactivation time constant (tau value) best described by two exponential fitting. The average data were presented as mean ± SD, n = 7–14 recordings. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus Pd1–3 for total Na+ currents. # P < 0.05 and ## P < 0.01 versus Pd7–10 for TTX‐R components. Scale bars in (C) also applied for (A) and (B).
