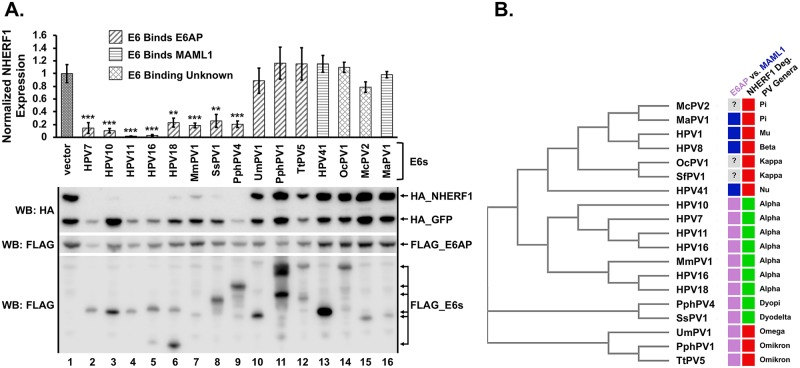
Fig 4. E6 proteins from evolutionarily diverse species target NHERF1.
(A) E6 proteins from divergent animal species degrade NHERF1 via E6AP. HA_NHERF1 (0.4 ug), HA_GFP (0.1 ug), FLAG_E6AP_WT (0.35 ug), and the indicated FLAG_E6 (0.3 ug) plasmids were co-transfected into C33A cells. E6 proteins are classified based on their known preference for binding E6AP or MAML as indicated. NHERF1 was degraded by E6 proteins isolated from numerous different mammalian species. Many, but not all, of the E6 proteins that bind E6AP targeted NHERF1 for degradation, while E6 proteins that bind MAML1 did not. HA_NHERF1 protein levels in the presence of the indicated E6 proteins were normalized to co-transfected HA_GFP as an internal transfection control. A single representative blot and the means of five independent experiments ± standard error are shown. N = 5, **<0.01, ***<0.001 by Student’s t-test. (B) E6 proteins that degrade NHERF1 cluster phylogenetically. The E6 proteins from the listed papillomaviruses were subjected to a multiple sequence alignment and then clustered phylogenetically using the program MUSCLE [66]. For E6 physical association, blue denotes MAML1 and light purple denotes E6AP. The preferential association of three E6 proteins is unknown. Ability to degrade NHERF1 is denoted in green and lack of ability to degrade NHERF1 is indicated by red. Interestingly, E6 proteins that can bind E6AP but not degrade NHERF1 cluster differently from other E6 proteins that cannot degrade NHERF1. The genera of each papillomavirus is listed. Western blot indicating NHERF1 expression in the presence of HPV1 E6, HPV8 E6, and SfPV1 E6 is shown in S3 Fig. H = Homo sapiens (human), Mm = Macaca mulata (rhesus monkey), Ss = Sus scrofa (wild boar), Pph = Phocoena phocoena (harbor porpoise), Um = Ursus maritimus (polar bear), Tt = Tursiops truncatus (bottlenose dolphin), Oc = Oryctolagus cuniculus (rabbit), Mc = Mastomys coucha (mouse), Ma = Mesocricetus auratus (golden hamster), Sf = Sylvilagus floridanus (Cottontail rabbit; CRPV1). Caption credit: Brimer N, Drews CM, Vande Pol SB. 2017. Association of papillomavirus E6 proteins with either MAML1 or E6AP clusters E6 proteins by structure, function, and evolutionary relatedness. PLoS Pathog 13:e1006781.