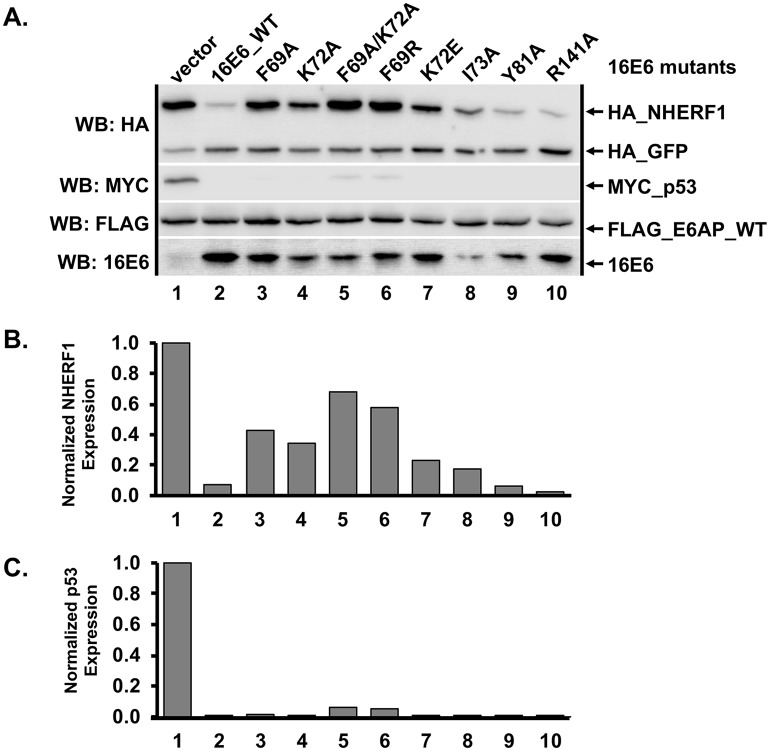
Fig 5. 16E6 mutagenesis screen identified mutants selectively defective in their ability to degrade NHERF1.
(A) Amino acids F69 and K72 are important for degradation of NHERF1 by 16E6. Plasmids encoding untagged 16E6_WT or 16E6 mutants (0.3 ug) were co-transfected with FLAG_E6AP (0.35 ug), HA_NHERF1 (0.4 ug), MYC_p53 (0.25 ug), and HA_GFP (0.08 ug) into C33A cells and HA_NHERF1 levels determined by western blot. Multiple 16E6 proteins were identified that were unable to degrade NHERF1 but were still capable of degrading p53. (B) HA_NHERF1 and (C) p53 protein levels were quantified and normalized to co-transfected HA_GFP as an internal transfection control.