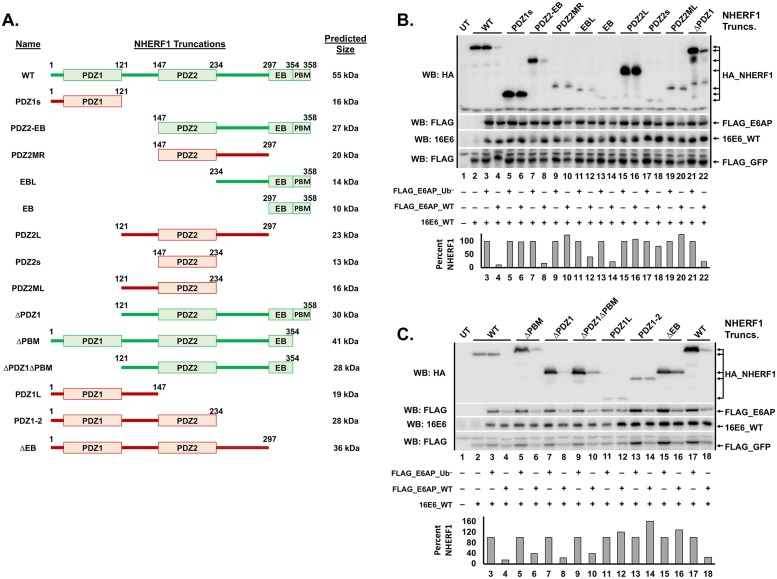
Fig 8. NHERF1 truncations identify the EB domain as necessary for NHERF1 degradation by 16E6.
(A) Schematic of NHERF1 truncations. NHERF1 proteins that were successfully degraded by 16E6_WT are depicted in green while truncations that were not degraded are depicted in red. (B and C) NHERF1 truncations containing the EB domain were degraded, while those lacking the EB domain were not. The listed HA_NHERF1 truncations (shown in A in the order loaded in B and C, 0.8 ug), untagged 16E6_WT (1 ug), FLAG_GFP (0.08 ug), and either FLAG_E6AP_WT (1.2 ug) or FLAG_E6AP_Ub− (1.2 ug, defective for ubiquitin ligase activity) were co-transfected in E6AP-null 8B9 cells. HA_NHERF1 levels were quantified and normalized to FLAG_GFP as an internal transfection control. The bar graph below the blot represents quantification of each listed HA_NHERF1 truncation. In panel C, the WT NHERF1 in lanes 2–4 contains an amino terminal 1X HA tag while the WT NHERF1 in lanes 17 and 18 contains an amino terminal 2X HA tag. All of the NHERF1 truncations contain amino terminal 2X HA tags. Levels of HA_NHERF1 truncations in the presence of FLAG_E6AP_WT were normalized to their corresponding expression in the presence of FLAG_E6AP_Ub− to account for the differing expression levels. UT = untransfected.