Figure 4.
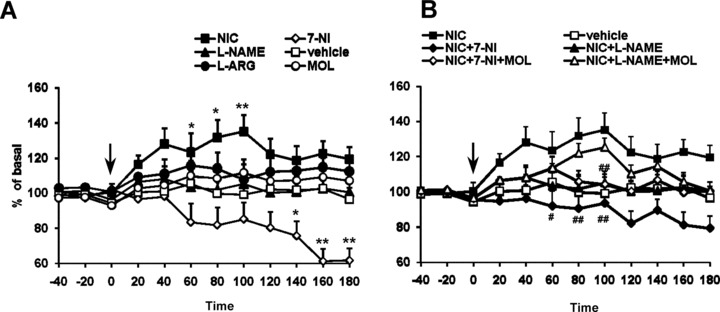
(A) Time course of the effect of acute nicotine (1 mg/kg, i.p.) administration on extracellular levels of DOPAC in the corpus striatum (n = 5). All the drugs and vehicle were injected at the time indicated by vertical arrow. Each data point represents mean ± SEM absolute levels of DA, without considering probe recovery. Statistical analysis shows a significant effect of nicotine and 7‐NI (one‐way ANOVA; P < 0.01) as compared with the control group. l‐NAME (50 mg/kg), MOL (50 mg/kg), and l‐ARG (50 mg/kg) did not modify at any time the DOPAC levels. (B) Time course of the blockade by 7‐NI and l‐NAME of the excitatory actions of nicotine (1 mg/kg, i.p.) administration on extracellular levels of DOPAC in the corpus striatum. The dose of 50 mg/kg i.p. 7‐NI and l‐NAME completely prevented nicotine‐induced increase in DOPAC release (two‐way ANOVA; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 by Tukey‐Kramer post hoc test).
