Figure 2.
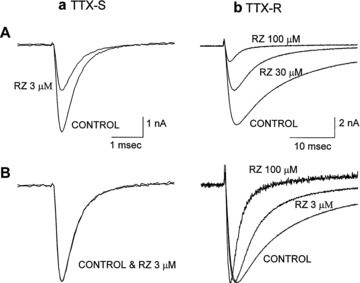
Effects of riluzole (RZ) on tetrodotoxin‐sensitive (TTX‐S) and tetrodotoxin‐resistant (TTX‐R) sodium channel currents of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Currents were evoked by depolarizing steps to 0 mV from a holding potential of −80 mV. TTX‐S currents activated and inactivated rapidly and were selectively blocked by 200 nM TTX, whereas TTX‐R currents activated and inactivated more slowly and were unaffected by 200 nM TTX. (a) TTX‐sensitive sodium channel. (b) TTX‐resistant sodium channel. (A) Riluzole blocks TTX‐sensitive sodium channel currents more potently than TTX‐resistant sodium channel currents when the membrane was held at −80 mV. (B) Peak current amplitude in the presence of riluzole is normalized to the control current. Riluzole did not alter the activation and inactivation kinetics of TTX‐S currents, while the time course of inactivation of TTX‐R currents was accelerated. Reprinted from [44], copyright (1997), with permission from the American Society for Experimental Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
