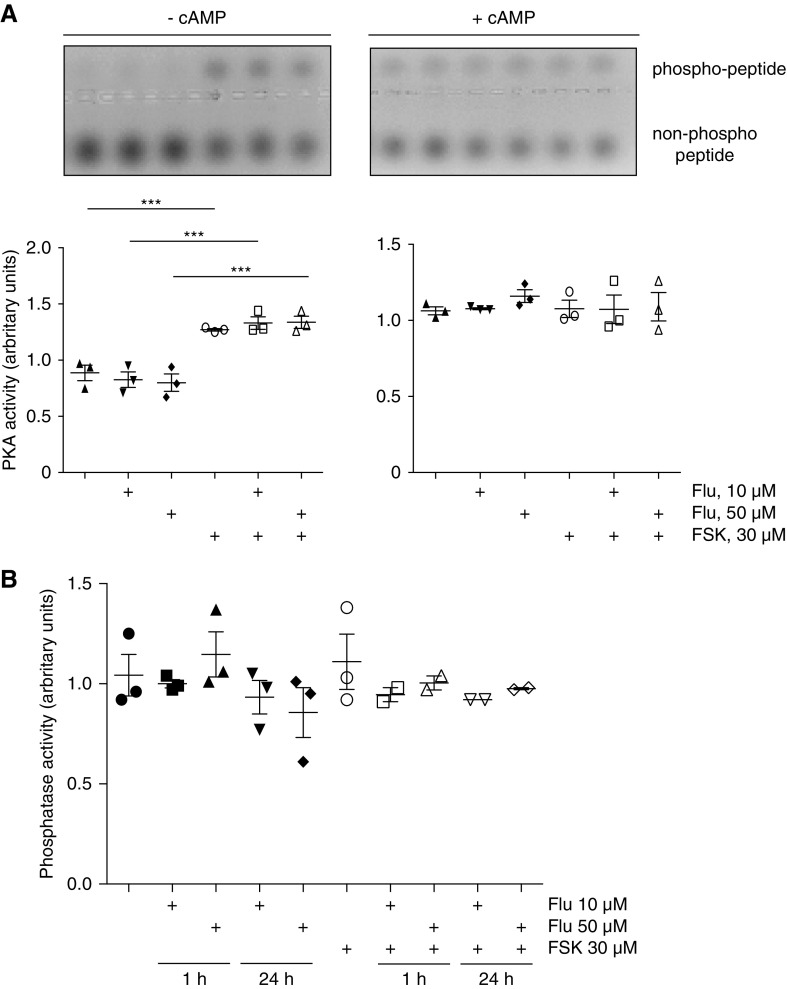
Figure 3.
Fluconazole (Flu) does not affect global protein kinase A (PKA) or protein phosphatase activity in inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD) cells. IMCD cells were left untreated, or they were stimulated with forskolin (FSK; 30 μM, 30 minutes), Flu alone or in combination with FSK for 1 hour in the indicated concentrations (FSK was added for the final 30 minutes). (A) Cell lysates were prepared, and PKA activity was determined by measuring its ability to phosphorylate the substrate peptide PepTag A1. Where indicated, cAMP (1 mM) was added to induce maximal PKA activity. PKA activity is expressed as the ratio of phosphorylated to nonphosphorylated PepTag A1 peptides. (Upper panels) Agarose gels from one representative of three experiments showing PKA-phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated PepTag A1 peptide. (Lower panels) The amounts of phosphorylated and nonphosphorylated PepTag A1 peptides were semiquantitatively analyzed. Statistically significant differences are indicated (mean±SEM). ***P<0.001. (B) IMCD cells were left untreated or stimulated with FSK, Flu alone, Flu in combination with FSK for 1 or 24 hours in the indicated concentrations. Lysates were prepared without phosphatase inhibitors, and amounts of 100 μg of proteins were loaded (each sample in triplicate in 96-well plate). The samples were incubated with substrate solution (10 mM para-Nitrophenylphosphate [pNPP]) for 30 minutes at 37°C, and absorbance was measured at 405 nm. The molar extinction coefficient for pNPP is 18,000 M−1 cm−1. The blank was subtracted to account for any phosphate release occurring in the absence of phosphatase. Shown are results from three independent experiments. There were no statistically significant differences found (mean±SEM).