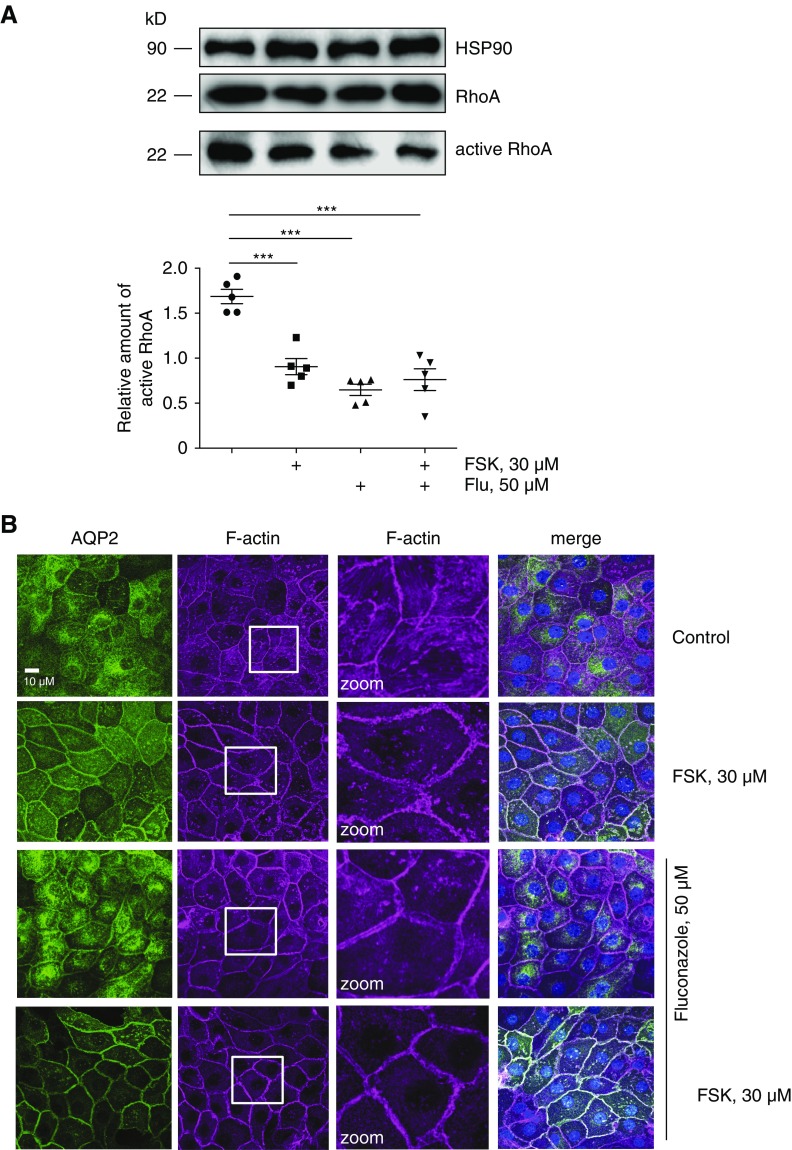
Figure 4.
Fluconazole (Flu) causes a decrease of RhoA activity and a depolymerization of F-actin in inner medullary collecting duct (IMCD) cells. (A) IMCD cells were left untreated or stimulated with forskolin (FSK), Flu alone, or Flu in combination with FSK for 1 hour in the indicated concentration. Lysates were prepared, and active RhoA was precipitated with Rhotekin beads. Precipitated active RhoA, RhoA in the lysates, and HSP90 as a loading control were detected by Western blotting using specific antibodies. The amount of active RhoA was related to normalized RhoA (RhoA in lysates to HSP90 [input]). Shown are representative blots from one of five independent experiments. Blots were semiquantitatively analyzed and statistically compared. Statistically significant differences are indicated (mean±SEM). ***P<0.001. (B) IMCD cells were left untreated or treated as indicated in A. Aquaporin-2 (AQP2) was detected by immunofluorescence microscopy using specific primary antibodies (H27) and Cy3-coupled anti-rabbit secondary antibodies (green), and F-actin was detected by using Alexa Fluor 647-Phalloidin (red). Nuclei were stained with 4′,6-diamidine-2′-phenylindole dihydrochloride (blue). The magnified views (zoom) of F-actin are from the indicated squares. Shown are representative images from one of three independent experiments.