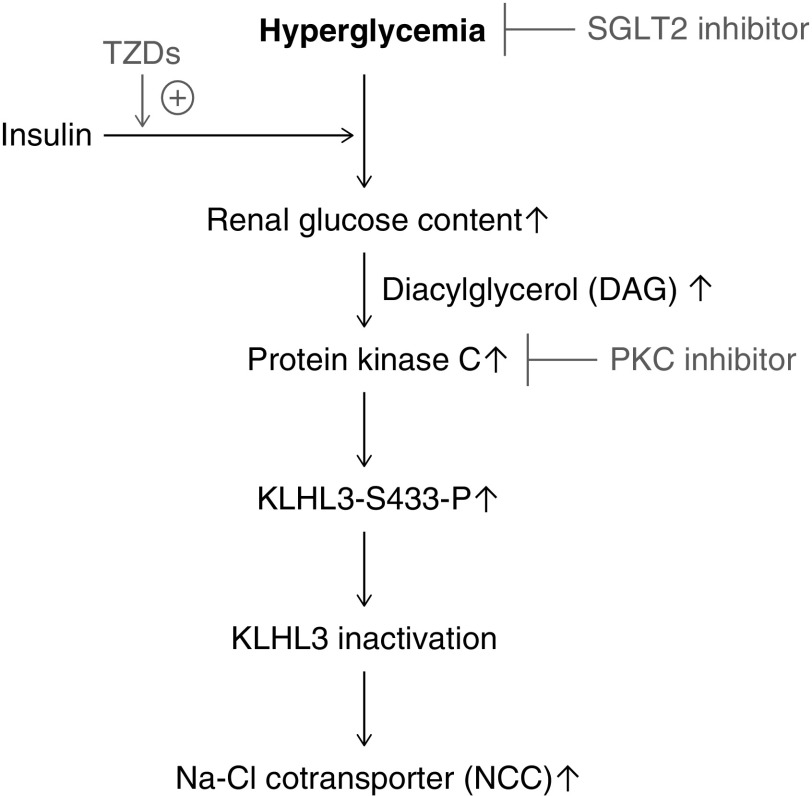
Figure 8.
High glucose-induced protein kinase C activation is involved in the dysregulation of Kelch-like 3 (KLHL3) and NaCl cotransporter (NCC) in the obese diabetic kidney. Hyperglycemia and cellular glucose accumulation can lead to increased protein kinase C (PKC) activity via the increased diacylglycerol (DAG) synthesis. Activated PKC, in turn, phosphorylates and inactivates the ubiquitin ligase component KLHL3 in the distal convoluted tubules, resulting in increased NCC activity and NaCl retention. Sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors effectively ameliorate this pathway by reducing blood glucose without stimulating cellular glucose uptake. Insulin and thiazolidinedione (TZD) also ameliorate hyperglycemia but can promote cellular glucose uptake.