Fig. 5. SNPs associated with nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate are highly enriched in enhancers established by p63 and KLF4.
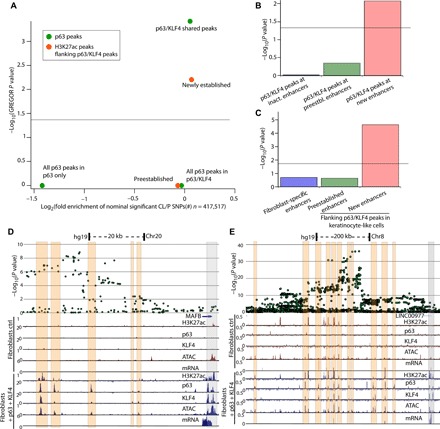
(A) GREGOR analysis showing that p63/KLF4 shared peaks (green) and newly established H3K27ac (orange) flanking these peaks are significantly (P < 0.05) enriched for SNPs associated with nsCL/P. (B) Colocalization of shared p63/KLF4 peaks at inactive (inact.)/preestablished (preestbl.)/new enhancers, with nominal significant nsCL/P-associated GWAS SNPs. The graph shows that only p63/KLF4 peaks flanked by de novo H3K27ac peaks are enriched for nsCL/P-associated SNPs. (C) Colocalization of H3K27ac peaks with nominal significant nsCL/P-associated GWAS SNPs. The graph shows that only new enhancers in converted cells flanking p63/KLF4 peaks are significantly enriched for nsCL/P-associated SNPs. (D and E) Overlay of SNPs and UCSC genome browser tracks highlighting (in orange) that p63/KLF4 peaks strongly colocalize with highly associated nsCL/P SNPs near MAFB and the known 8q24 locus; binding of both proteins at promoters is highlighted in gray.
