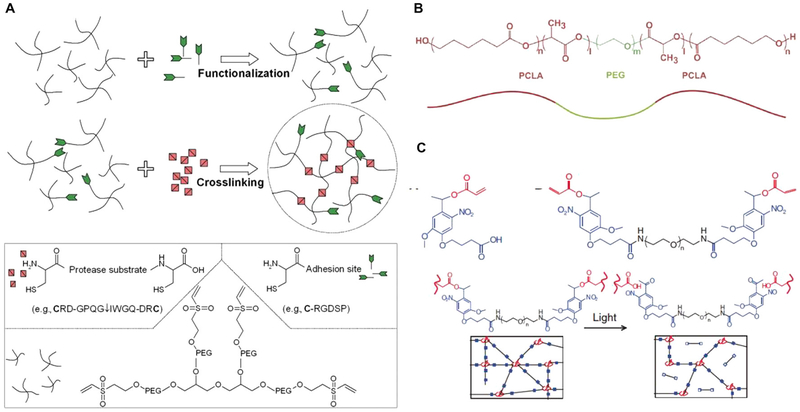
Figure 23.
Hydrogels with different degradation mechanisms. (A) An enzymatically degradable PEG-based hydrogel. Vinyl sulfone-modified multiarm PEG macromers are functionalized with cell adhesion peptides and then cross-linked with bis-cysteine MMP-sensitive peptides to form enzyme-degradable hydrogels. Reprinted with permission from ref 838. Copyright 2003 Nature Publishing Group. (B) Molecular structure of a hydrolytically degradable triblock copolymer, i.e., PCLA-PEG-PCLA. Reprinted with permission from ref 839. Copyright 2011 Elsevier, Ltd. All rights reserved. (C) A photodegradable PEG-based hydrogel. Such a photodegradable hydrogel system has been used for engineering softening hydrogels. Reprinted with permission from ref 459. Copyright 2009 American Association for the Advancement of Science.