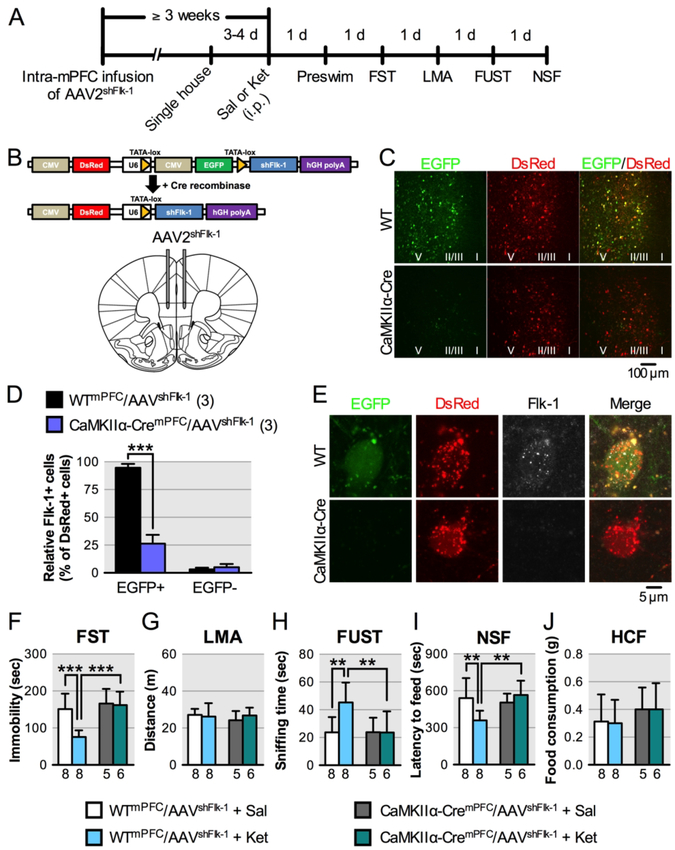
FIGURE 4. Effect of local knockdown of Flk-1 in mPFC pyramidal neurons on the behavioral effects of ketaminea.
a(A) Experimental timeline for behavioral testing starting ≥ 3 weeks after intra-mPFC infusion of AAV2shFlk−1 and 1 day after i.p. injection of either saline or ketamine (10 mg/kg). (B) Diagram of pshFlk-1 construct and Cre-induced recombination enabling U6 driven expression of shFlk-1. AAV2shFlk−1 was bilaterally infused into the mPFC of WT or CaMKIIα-Cre mice. (C) Representative images of the mPFC of WTmPFC/AAV2shFlk−1 (n = 16) and CaMKIIα-CremPFC/AAV2shFlk−1 mice (n = 11). Approximate laminar regions (I-V) are noted. (D) The relative number of Flk-1+/EGFP+/DsRed+ (t4 = 13.7, p = 0.0002) and Flk-1+/EGFP-/DsRed+ cells (t4 = 1.06, p = 0.348) in the mPFC of WTmPFC/AAV2shFlk−1 (n = 3; 54.7 ± 22.3 DsRed+ cells/mouse (total 164 cells) were analyzed) and CaMKIIα-CremPFC/AAV2shFlk−1 mice (n = 3; 62.3 ± 12.1 DsRed+ cells/mouse (total 187 cells) were analyzed). (E) Representative images of EGFP, DsRed expression and Flk-1 immunolabeling in mPFC neurons from WTmPFC/AAV2shFlk−1 and CaMKIIα-CremPFC/AAV2shFlk−1 mice. (F) Immobility time in the forced swim test (FST) 2 days after i.p. injection (interaction, F1,23 = 6.88, p = 0.015, n = 5–8). (G) Locomotor activity (LMA) 3 days after i.p. injection (interaction, F1,23 = 0.776, p = 0.39, n = 5–8). (H) Time spent sniffing female urine in the female urine sniffing test (FUST) 4 days after i.p. injection (interaction, F1,23 = 4.51, p = 0.045, n = 5–8). (I) Latency to feed in the novelty-suppressed feeding test (NSF) 5 days after i.p. injection (interaction, F1,23 = 6.84, p = 0.016, n = 5–8). (J) Home cage feeding (HCF) just after the NSF (interaction, F1,23 = 0.00778, p = 0.93, n = 5–8). Data are expressed as means ± SD. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.