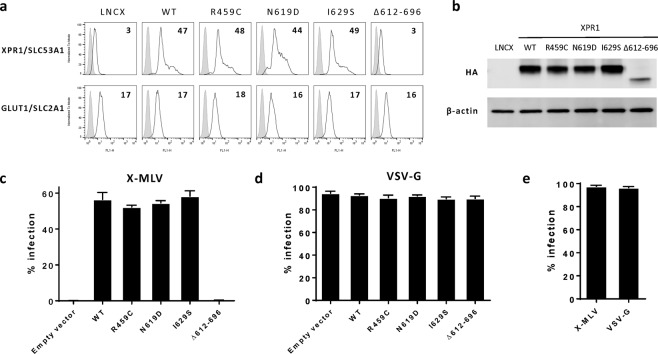
Figure 3.
PFBC XPR1/SLC53A1 variants do not alter virus entry. (a) Cell surface detection of XPR1/SLC53A1 (upper panel) and GLUT1/SLC2A1 (lower panel) in CHO hamster cell populations stably expressing the control parental expression vector lacking XPR1/SLC53A1 (LNCX), or encoding either WT XPR1/SLC53A1, or variants p.R459C, p.N619D or p.I629S, or the p.(L612_T696del) deletion mutant. Cells were assayed for XPR1/SLC53A1 and GLUT1/SLC2A1 surface expression with their corresponding XRBD and H2RBD ligands, respectively. Numbers indicate the specific delta mean fluorescence intensity of a representative experiment (n = 3), as compared to non-specific staining with the secondary IgG (grey histograms). (b) Representative immunoblot of HA-tagged XPR1/SLC53A1-containing cell lysates from (a) with an anti-HA antibody (upper panel), or with an anti β-actin antibody used as loading control (lower panel). (c) Analysis of viral infection in CHO cells stably expressing either of WT or XPR1/SLC53A1 variants. Cells were assayed for infection with retroviral vectors pseudotyped with X-MLV Env or (d) VSV-G. Two days after infection, cells were analyzed by flow cytometry. Graphics are average values from 3 different wells in one representative experiment (n = 3). (e) Infectivity of viral supernatants on control HEK293T susceptible cells.