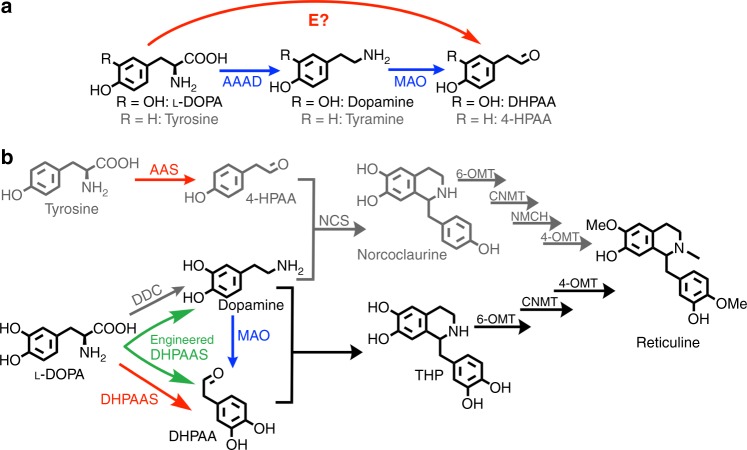
Fig. 1.
Design of a symmetrical THP pathway for reticuline bioproduction. a M-path enzyme (E) search identified phenylacetaldehyde synthase (PAAS), 4-HPAA Synthase (4-HPAAS), and DHPAAS as putative enzymes to directly produce 4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (4-HPAA) from tyrosine or DHPAA from L-DOPA (Supplementary Table 1). b Multiple pathways lead to THP and norcoclaurine production, including a nonsymmetrical DDC-MAO-mediated pathway (blue and grey arrows), symmetrical DDC-DHPAAS/AAS-mediated pathways (red and grey arrows), and an engineered DHPAAS single enzyme system (green split arrows). (S)-norcoclaurine can be produced from 4-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde (4-HPAA) and dopamine via the enzyme (S)-norcoclaurine synthase (NCS, EC 4.2.1.78). Dopamine and DHPAA undergo spontaneous Pictet-Spengler condensation to form THP (3-hydroxy-norcoclaurine), or this reaction can also be catalyzed by NCS. THP is converted to reticuline via norcoclaurine 6-O-methyltransferase (6-OMT), coclaurine N-methyltransferase (CNMT) and 3-hydroxy-N-methylcoclaurine 4-O-methyltransferase (4-OMT). An additional enzyme, N-methylcoclaurine 3-hydroxylase (NMCH), is necessary to produce reticuline from norcoclaurine. The 4-HPAA containing pathways are shown in grey as the current study focuses on the DHPAA containing pathway. All structures were drawn with ChemDraw