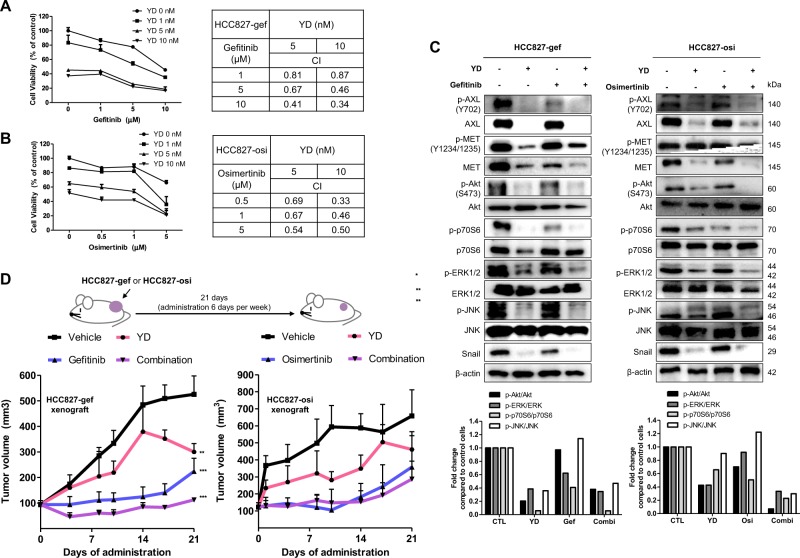
Fig. 4. YD and EGFR-TKIs synergistically inhibit the growth of gefitinib and osimertinib cross-resistant cells in in vitro and in vivo.
Cell viability was measured after combined treatment of YD and gefitinib or osimertinib for 72 h in HCC827-gef (a) and HCC827-osi (b), respectively. Based on the cell viability results, CI values were calculated to demonstrate the combination effects in each cell line. The effects of combination treatment compared with single treatment were accessed using western blot. Cells were treated with YD (10 nM) and/or gefitinib (1 μM) in HCC827-gef cells, and YD (10 nM) and/or osimertinib (500 nM) in HCC827-osi cells (c). HCC827-gef cells were subcutaneously implanted into the flanks of Balb/c-nude mice (n = 5). Mice were orally administered with compounds 6 times per week for 21 days and doses indicated are 1 mg/kg for YD, 10 mg/kg for gefitinib. HCC827-osi cells were subcutaneously implanted into the flanks of Balb/c-nude mice (n = 5). Mice were orally administered with compounds 6 times per week for 21 days and doses indicated are 0.5 mg/kg for YD, 5 mg/kg for osimertinib (d). Data are presented as the mean fold changes ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005 by t-test