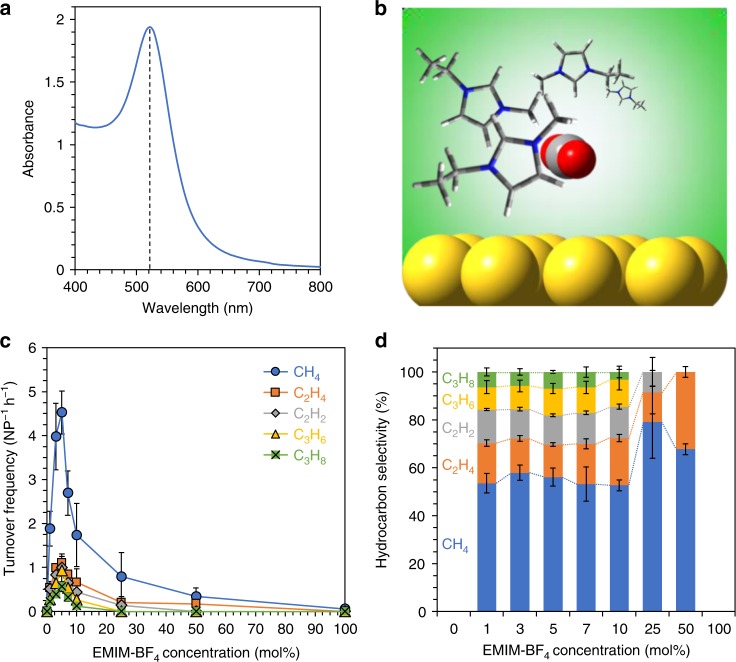
Fig. 1.
Ionic-liquid-promoted CO2 reduction to C1–C3 hydrocarbons using a plasmonic Au nanoparticle (NP) photocatalyst. a UV−vis extinction spectrum of a colloid of the Au NPs used for preparation of the photocatalyst film. The spectrum exhibits a localized surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) band centered around 520 nm, as indicated by the dotted line. b Scheme for CO2 conversion on plasmon-excited Au NPs promoted by an ionic liquid, EMIM-BF4. A continuous-wave (CW) laser of a wavelength of 532 nm and intensity of 1 W cm–2 was used as the light source for photoexcitation of Au NPs. EMIM-BF4 stabilizes CO2 and resulting adsorbates/intermediates on the photoexcited Au surface. c Turnover frequencies of hydrocarbon products formed in the CO2RR plotted as a function of the EMIM-BF4 concentration (mol%). The CO2 conversion activity peaks at 5 mol% of EMIM-BF4. d Hydrocarbon product selectivity as a function of EMIM-BF4 concentration (mol%). Each data point in c and d is the average of results from three identical trials and the error bar represents the SD of these measurements