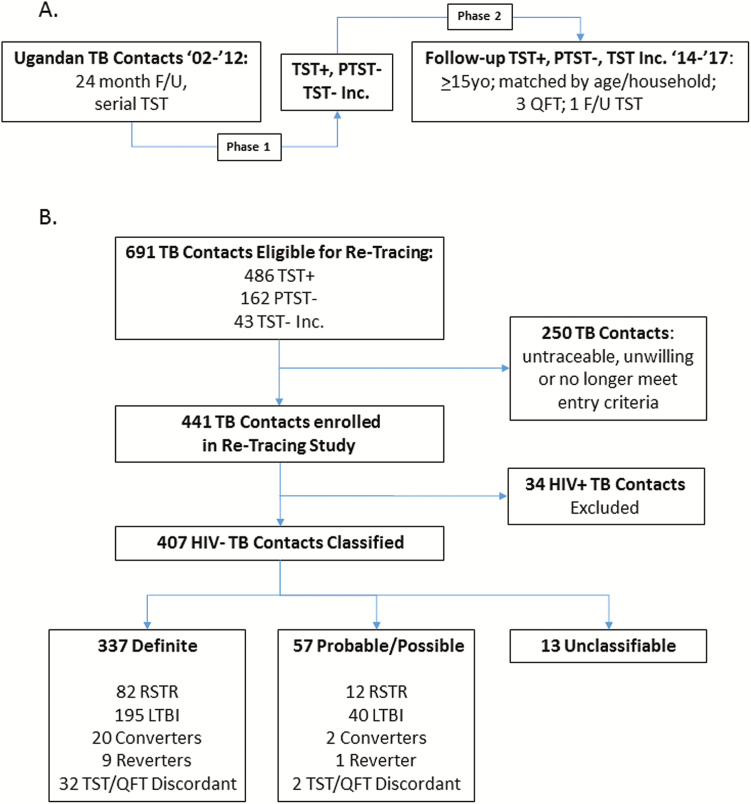
Figure 1.
Retracing study design and classification of retraced TB household contacts. A, Study design: TB household contacts with either persistently negative tuberculin skin tests (PTST−) or latent M.tb infection (LTBI) were identified in Kampala, Uganda between 2002 and 2012 (phase 1* [12]). PTST− and LTBI contacts from phase 1 were identified for retracing between 2014 and 2017, if they were > 15 years old in 2014, and matched by age bracket and household. Retraced contacts underwent 3 QFT tests and 1 TST (phase 2) over 1–2 years of additional follow-up. B, Classification of retraced contacts: PTST−, LTBI, or TST− contacts with less than 12 months of follow-up (TST incomplete [Inc]) in phase 1 were retraced and classified, based on 3 QFT from phase 2 and 2 TST from phases 1 and 2, into resister (RSTR; all tests negative), LTBI (all tests positive), converter (TST− in phase 1, QFT+/TST+ in phase 2), reverter (TST+ Inc phase 1, QFT−/TST−Inc phase 2) or TST/QFT discordant (TSTs consistent, QFTs consistent but in opposing directions). Among 250 subjects not consented, 6 had developed active TB between phases 1 and 2, 32 declined consent, 39 were unavailable, and 173 were untraceable. Contacts who developed TB were not eligible for retracing. The 34 HIV+ subjects excluded from further analysis included 27 who were HIV+ in phase 1 and 7 HIV conversions between phases 1 and 2. Classification as definite was based on availability and consistency of all 5 measures (2 TST and 3 QFT). Probable or possible classification was used when 1 assay was missing or equivocal. Unclassifiable subjects either didn’t complete phase 2 or had very inconsistent TST and QFT results (see Suppl. Methods). Abbreviations: F/U, follow up; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; QFT, quantiferon-TB Gold; RSTR, resister phenotype; TB, tuberculosis; TST, tuberculin skin test.