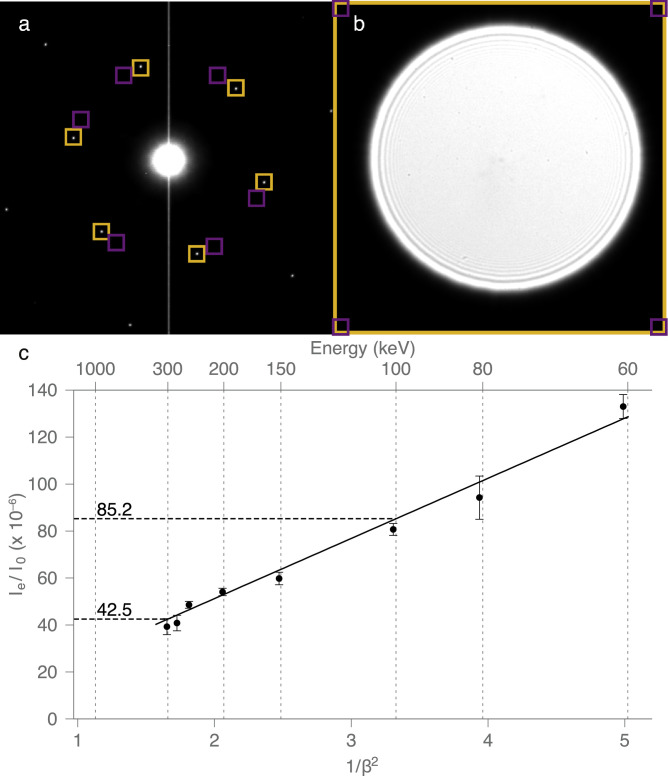
Fig. 1.
Elastic scattering cross-section vs. energy for carbon in the form of graphene. A typical diffraction pattern is shown in (a) where the orange boxes surround the first order Bragg reflections at 1/2.14 Å. To measure the intensity of this peak (taken as Ie, the intensity of elastic scattering), the sum of the pixel values in the box was subtracted from an adjacent box (purple) at the same radius. This was then compared to the forward scattered central beam intensity I(0,0) using I0 = Ie + I(0,0) (b) defocusing the (0,0) spot prevented saturation of the detector and background intensity was determined from measurements at the corners of the image (of the diffraction pattern). The ratio of the first reflection to the forward scattered beam is plotted vs 1/β2 in (c), where β is the ratio of the electron speed to that of light and the error bars are the standard deviation of three measurements at each energy.