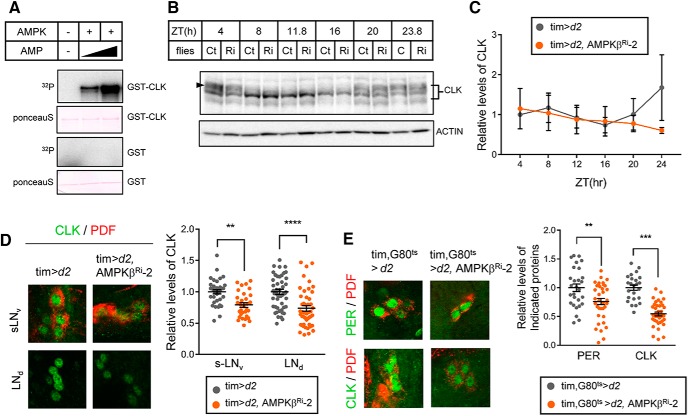
Figure 6.
AMPK directly phosphorylated CLK in vitro and stabilized CLK in clock neurons. A, GST-CLK and GST purified from E. coli were incubated with AMPK holoenzyme and γ-32P-ATP with increasing amounts of AMP. The samples were then subjected to SDS-PAGE, and the proteins were transferred to PVDF membranes. Following Ponceau S staining, phosphorylation of GST-CLK and GST was visualized by autoradiography. B, Protein extracts from the heads of control (Ct) and AMPKβ knockdown flies (Ri) were prepared at the indicated ZT and were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-CLK (gp208) antibody. Actin served as the loading control. C, Relative levels of CLK were determined by measuring band intensities using ImageJ software. Values indicate mean ± SEM (n = 3). D, Flies of the indicated genotypes were collected at ZT24 during LD, and the brains were stained with antibodies to CLK (gp50, green) and PDF (C7, red). Representative images of sLNvs and LNds from two independent experiments are shown. CLK fluorescence intensities were quantified. Values indicate mean ± SEM (n = 24–53). Statistically significant differences between control and AMPKβ Ri flies (Student's t test): **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001. E, Flies of the indicated genotypes were collected at ZT2 at 29°C. The brains were costained with antibodies to CLK (gp50, green) and PDF (C7, red) or PER (Rb1, green) and PDF (C7, red). Representative images of sLNvs are shown. CLK and PER fluorescence intensities were quantified. Values indicate mean ± SEM (n = 24–37). Statistically significant differences between control and AMPKβ Ri flies (Student's t test): **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.