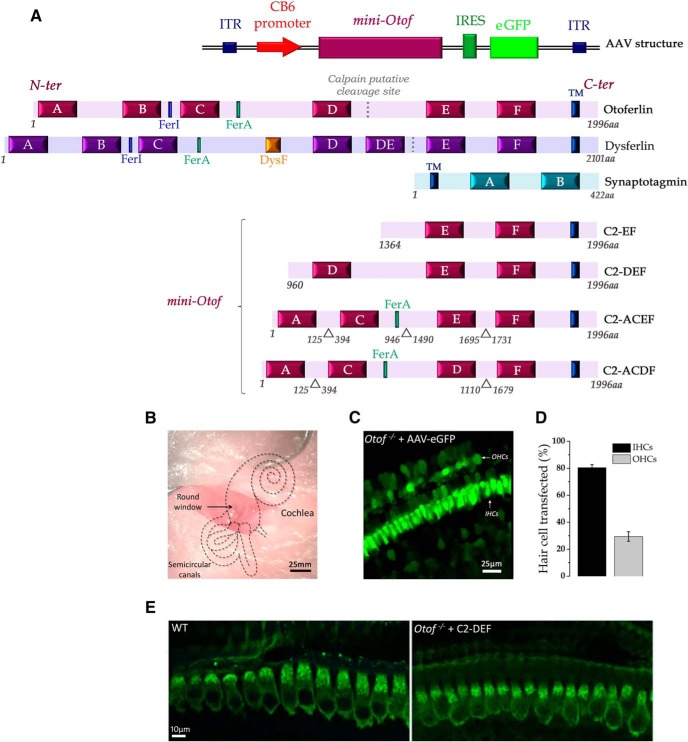
Figure 1.
Comparative structure of the native otoferlin and the four different mini-otoferlins inserted in the AAV vector to evaluate their role in hearing and IHC exocytosis. A, Otoferlin is a large protein (∼2000 amino acids) that contains a single TM domain at its C-terminal part, a FerA domain, and six C2 domains (C2-A to C2-F) that potentially bind calcium (Ca2+) and interact with phospholipids. Dysferlin, a dystrophy-associated Fer-1-like protein, contains seven C2 domains, a FerA domain, and a DysF domain. The dotted lines in the otoferlin and dysferlin sequences indicate a putative calpain cleavage site (Lek et al., 2012; Redpath et al., 2014). Synaptotagmins, the major Ca2+ sensors in CNS synapses, which are absent in IHCs synapses (Beurg et al., 2010), contain only two C2 domains. Note that in humans, a short isoform of otoferlin with three C2-domains (C2-DEF) and a FerA domain with unknown function has been identified (Yasunaga et al., 1999). The putative function of these truncated mini-otoferlins, C2-EF and C2-DEF, in IHC exocytosis remains unknown. Also, two abridged otoferlin-like containing C2-ACEF or C2-ACDF constructs (∼30% smaller than the native otoferlin) were tested. The AAV8 sequence contains a promoter CB6 that allows the expression of the short otoferlins (C2-EF, C2-DEF, C2-ACEF or C2-ACDF domains) and the eGFP reporter (only for C2-EF) in IHCs. (ITR as Inverted Terminal Repeat sequences). B, AAVs are injected in vivo through the round window of the cochlea at P1–P3. C, For C2-EF, the successful AAV infection of IHCs was verified with the fluorescent reporter eGFP. D, Rates of transfection for IHCs and OHCs, respectively. Error bars indicate SE. E, The expression of the mini-otoferlin C2-DEF in Otof−/− IHCs was verified by immunoconfocal imaging with a C-terminal otoferlin antibody. Note that the expression of C2-DEF was similar to that of the native otoferlin in WT IHCs.