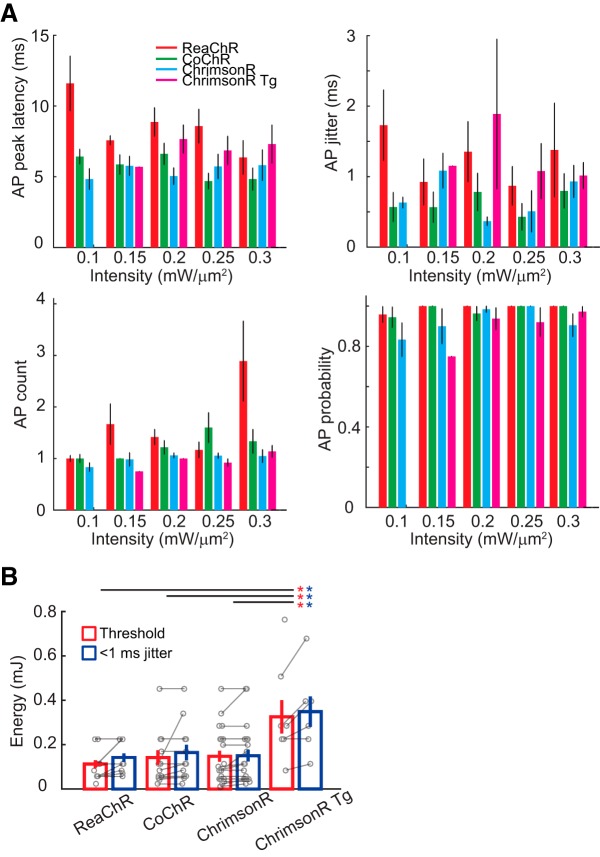
Figure 2.
AP induction in response to different illumination intensities. A, Holography-induced spike properties of peak latency, jitter, AP count, and AP probability per stimulus in vivo as a function of excitation intensity (n = 8, 6, 9, 6, 3 for ReaChR upon photostimulation of 0.1, 0.15, 0.2, 0.25, 0.3 mW/μm2; n = 6, 8, 9, 5, 5 for CoChR, n = 4, 4, 16, 6, 7 for ChrimsonR, and n = 0, 1, 4, 5, 6 for ChrimsonR Tg of respective excitation intensity). B, Required energy using light pulses of 0.1–0.45 mW/μm2, 2–15 ms, for reaching spike threshold and submillisecond jitter (n = 15, 13, 24, 8 for ReaChR, CoChR, ChrimsonR, and ChrimsonR Tg respectively). Significant difference in energy-reaching threshold and <1 ms jitter is respectively denoted as red and blue asterisks for multiple comparisons between opsin types.