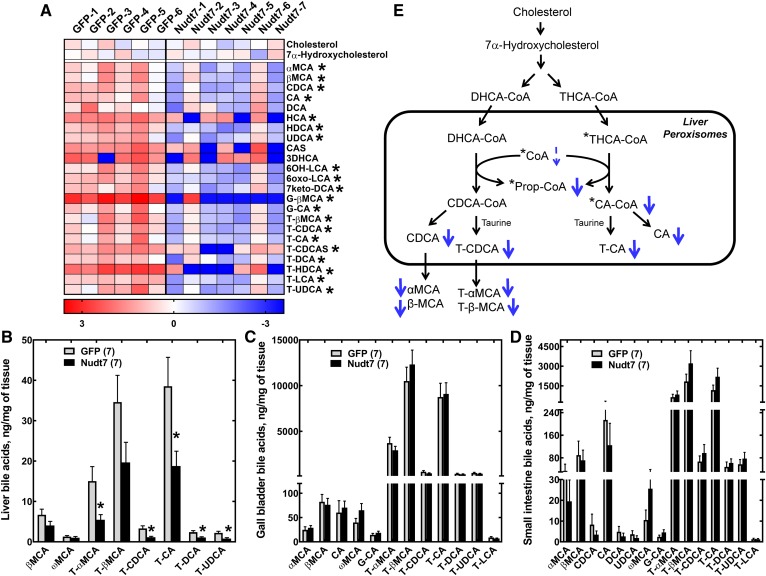
Fig. 5.
Nudt7 overexpression in the fasted state decreases the hepatic bile acid content. A: Heat plot of all primary and secondary bile acids, plus the bile acid precursors, cholesterol and 7α-hydroxycholesterol, detected by global metabolic profiling. Targeted bile acid analysis of livers (B), gall bladder extracts (C), and small intestine (D). In B–D, data are reported as the mean ± SEM and numbers in parenthesis represent the number of animals analyzed. *P < 0.05. E: Scheme of the conversion of DHCA-CoA and THCA-CoA to chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) and cholic acid (CA) derivatives in the peroxisomes. Known substrates of Nudt7 are marked by an asterisk. Overexpression of Nudt7 was associated with a decrease (thick blue arrows) in the concentration of choloyl-CoA (CA-CoA), propionyl-CoA (Prop-CoA), and of several primary and secondary bile acids, as detected by either untargeted or targeted bile acid analyses. The decrease in free CoA, which narrowly missed statistical significance (P = 0.07), is indicated by the thin dashed arrow. CA, cholic acid; CAS, cholic acid sulfate; CDCA, chenodeoxycholic acid; DCA, deoxycholic acid; 7keto-DCA, 7-keto-deoxycholic acid; HDCA, hyodeoxycholic acid; 3DHCA, 3-dehydrocholic acid; 6OH-LCA, 6-hydroxy-lithocholic acid; 6oxo-LCA, 6-oxo-lithocholic acid; G-CA, glycocholic acid; G-βMCA, glyco-β-muricholic acid; HCA, hyocholic acid; HDCA, hyodeoxycholic acid; LCA, lithocholic acid; αMCA, α-muricholic acid; βMCA, β-muricholic acid; ωMCA, ω-muricholic acid; T-CA, taurocholic acid; T-CDCA, taurochenodeoxycholic acid; T-CDCAS, taurochenodeoxycholic acid sulfate; T-DCA, taurodeoxycholic acid; T-αMCA, tauro-α-muricholic acid; T-βMCA, tauro-β-muricholic acid; T-LCA, taurolithocholic acid; T-HDCA, taurohyodeoxycholic acid; T-UDCA, tauroursodeoxycholic acid; UDCA, ursodeoxycholic acid.