Figure 1.
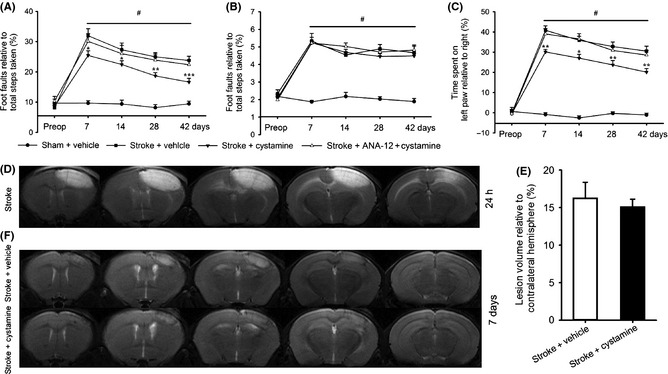
Effect of cystamine on the functional recovery and infarct size after stroke. Cystamine treatment starting from 24 h after stroke resulted in a time‐dependent improvement in functional recovery after stroke. Functional recovery was assessed with the grid‐walking task for forelimb foot faults (A) and hindlimb foot faults (B), and the cylinder task for forelimb asymmetry (C). Data are shown as mean ± SEM for n = 8 per group. #P < 0.001 for stroke + vehicle versus sham, *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 versus stroke + vehicle using two‐way ANOVA with repeated measures and Newman–Keuls' multiple pair‐wise comparisons. Representative focal infarcts are shown on T2‐weighted images at 24 h after photothrombotic focal stroke (D). Quantification of the lesion volume (E) and representative focal infarcts on T2‐weighted images (F) from the mice treated with or without cystamine groups at 7 days after stroke. Data are shown as mean ± SEM for n = 8 per group. t[15] = 1.25, P = 0.229 versus stroke + vehicle group using Student's t‐test. Preop = preoperation.
