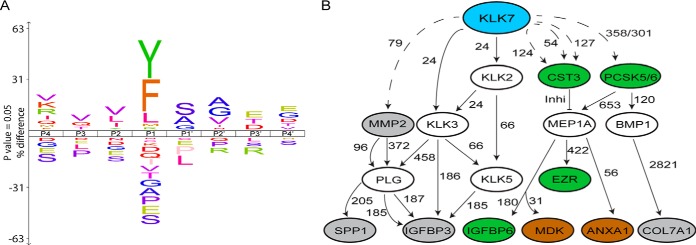
Fig. 4.
KLK7 subsite preferences and potential role in the greater proteolytic web. A, To determine KLK7 subsite preferences, TAILS-identified cleavage sites are displayed as IceLogos representation by comparing both the positive and negative frequency percentage of an amino acid (vertical axis) at a certain location in the multiple sequence alignment (horizontal axis) and the Swiss-Prot Homo sapiens protein database. KLK7 showed chymotryptic-like specificities by cleaving C-terminal to tyrosine (Y), phenylalanine (F) and leucine (L). The height of the single amino acid residue reflects its occurrence rate for each position in P4-P4′. Amino acid residues are color coded according to their physico-chemical properties. Sequence logo x axis indicates percent difference at a p value of 0.05%. B, Potential association of KLK7 with TAILS-identified (11) substrates, determined using the TopFINDer (v3.0) software. Blue oval, protease of interest, KLK7; gray ovals, TAILS-identified KLK7 substrates in SKOV-3 cell line; brown ovals, TAILS-identified KLK7 substrates in OVMZ-6 cell line; green ovals, TAILS-identified substrates in both cell lines; open ovals, KLK7 substrates known to date and putative intermediate proteins; dotted line, cleavages identified in TAILS; solid lines, recorded cleavage events in MEROPS; and numbers, amino acid residues at cleavage sites.