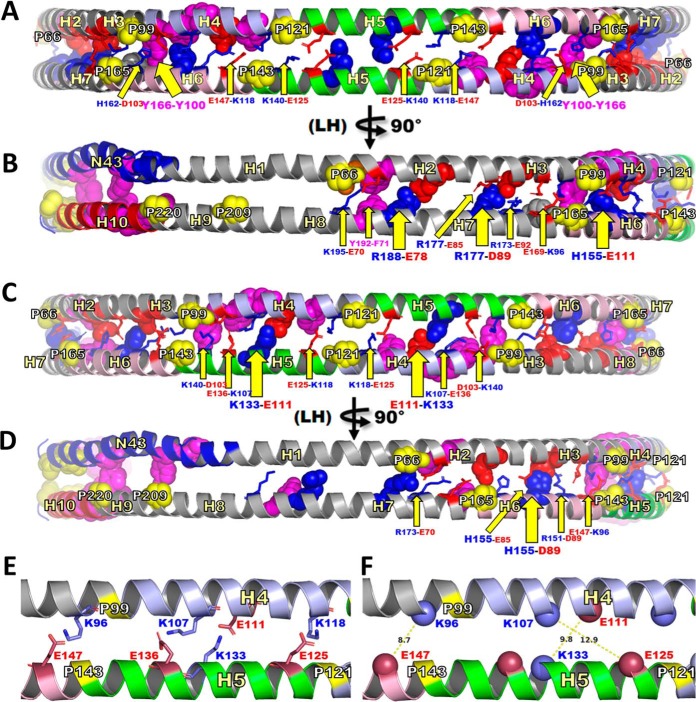
Fig. 5.
Schematic representation of residues proposed to form salt bridges that stabilize dimerization of LL5/5 and LL5/4 antiparallel double belt structures. This figure is a molecular representation of LL5/5 and LL5/4 highlighting residues positioned to form interchain salt bridges and other types of bonds (such as π-π interactions). To maximize the formation of potential interchain salt bridges and other types of bonds, the idealized circular LL5/5 and LL5/4 structures were subjected to molecular dynamic simulation in vacuo for 1 ns after fixing all backbones and sidechains except sidechains in the wp2, wp5 and wp9 positions (55). A, Schematic molecular representation of LL5/5 centered on the disc edge and pairwise antiparallel H5s to create a bilaterally symmetric view. B, Same view as A rotated 90° in left hand (LH) direction. C, Schematic molecular representation of LL5/4 centered on the disc edge and pairwise antiparallel H5/4s to create a bilaterally symmetric view. D, Same view as C rotated 90° in left hand (LH) direction. E and F, represent an enlargement of the cartoon molecular representation of C focused on the left hand half to illustrate Cα-Cα distances of the observed K96-E147, K107-E125 and K133-E111 cross-links. E, Four residue pairs forming salt bridges. F, Measurement of distances between Cα-Cα atoms of the K96-E147, K107-E125 and K133-E111 cross-links. Solvent-accessible salt bridge residues, stick representation indicated with narrow yellow arrows and smaller labels. Solvent-inaccessible salt bridge residues, space filling representation indicated with wide yellow arrows and larger labels. Tandem helical repeats: D1-N43, blue; H2-H3, gray; H4, light blue; H5, green; H6, light pink H7-H9, gray; H10, red. Basic residues, blue; acidic residues, red; prolines, space filling yellow; aromatic residues, space filling magenta.