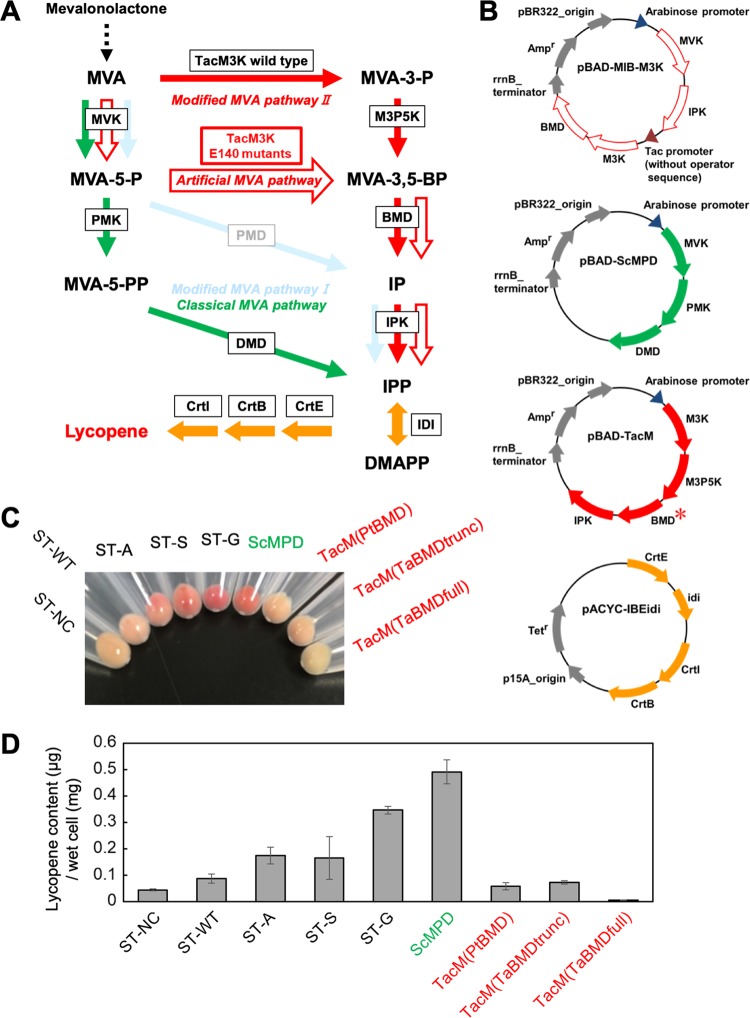
FIG 6.
Carotenoid production in E. coli strains that possess an artificial MVA pathway. (A) Scheme of lycopene biosynthesis via the artificial or known MVA pathways. The artificial MVA pathway is indicated by red open arrows. The known MVA pathways utilized to construct the strains for comparison are colored as in Fig. 1, and the unused modified MVA pathway I is also indicated. The enzyme catalyzing each reaction is boxed. (B) The plasmids used to construct the lycopene-producing strains. Detailed information about the inserted genes is provided in Table 2. A red asterisk means that the BMD gene from P. torridus or T. acidophilum (in the full-length or truncated form) was used to construct the pBAD-TacM plasmid series. (C) The cell pellets of the strains used, as indicated. (D) Amounts of lycopene extracted from the strains. Cultivation of each strain and extraction of lycopene from the cells were performed in triplicate. DMAPP, dimethylallyl diphosphate.